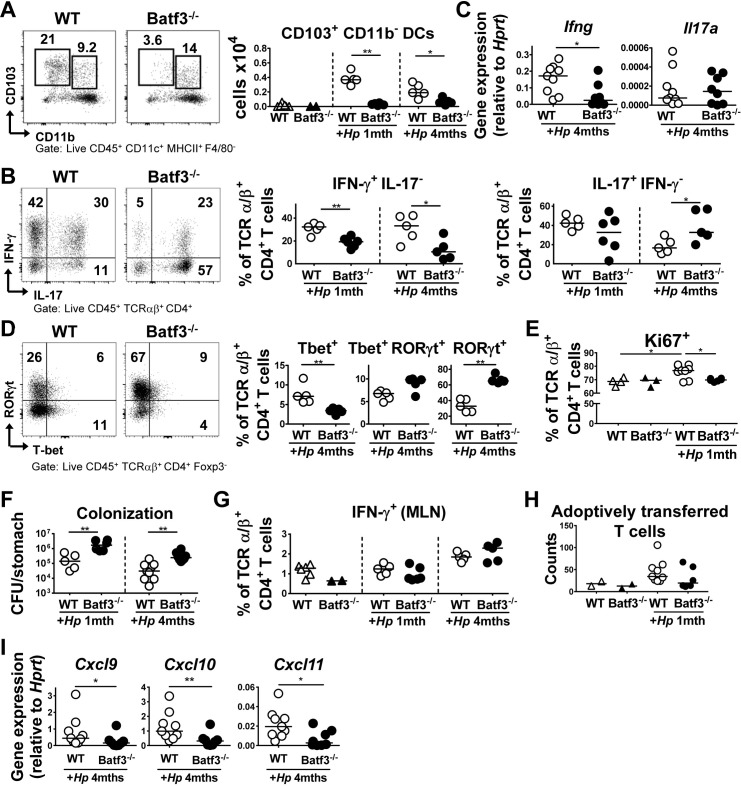
Fig 1. BATF3-dependent DCs are required for local Th1 responses and bacterial infection control.
(A-D) BATF3-/- and WT mice were infected with H. pylori and their gastric LP leukocytes were analyzed by FACS at one or four months p.i. (A) Absolute counts of CD103+ CD11b- DCs in the gastric LP of naïve and infected WT and BATF3-/- mice. Representative FACS plots are shown alongside summary plots. (B) Frequencies of IFN-γ+ and IL-17+ CD4+ T-cells of the mice shown in A. The summary plot shows a representative time course of three independently conducted experiments. (C) Expression of IFN-γ and IL-17 in the gastric mucosa of WT and BATF3-/- mice at four months p.i.; results are pooled from two independent experiments. (D) RORγt and Tbet expression of LP CD4+ T-cells of the mice shown in A at four months p.i. (E) Mice of the two genotypes were infected as described above, and subjected to Ki67 staining of their LP T-cells. Results are from one experiment. (F) H. pylori colonization of the mice shown in A-D. (G) IFN-γ expression of CD4+ T-cells in the MLNs of WT and BATF3-/- mice infected with H. pylori for 1 and/or 4 months as shown in A. Results are representative of two independent experiments. (H) Absolute numbers of adoptively transferred CD45.1+ CD4+ T-cells recovered from the gastric LP of recipients of the indicated genotypes five days post adoptive transfer. Naïve recipients of T-cells are shown as controls alongside H. pylori-infected recipients. (I) Expression of CXCL9, 10 and 11 in the gastric mucosa of WT and BATF3-/- mice four months p.i.; results are pooled from two independent experiments.