Figure 2.
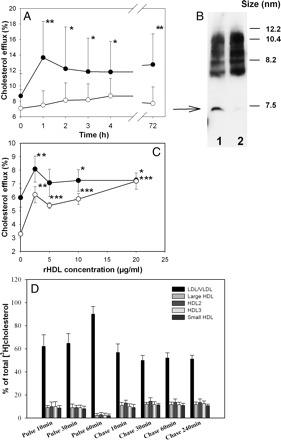
Contribution of apoB-containing lipoproteins to enhanced capacity of plasma to support cholesterol efflux. (A) Changes in the capacity of whole patient plasma and apoB-depleted plasma to support cholesterol efflux. Mean ± SD are shown; n = 13. *P < 0.050, **P < 0.005. (B) Distribution of apoA-I among HDL subfractions before (1) and after (2) precipitation of apoB-containing lipoproteins. (C) Dose dependence of cholesterol efflux from THP-1 cells to whole human plasma (closed symbols) or apoB-depleted plasma (open symbols) supplemented with indicated concentrations of rHDL. Mean ± SD of quadruplicate determinations are shown. *P < 0.050, **P < 0.015, ***P < 0.001 (vs. before infusion). (D) The distribution of labelled cholesterol between lipoprotein fractions after pulse-chase experiment. The values shown are percentages of labelled cholesterol in each fraction relative to the total amount of released [3H]cholesterol (this normalization was necessary to permit comparisons among samples with a wide range of total labelled cholesterol). Means ± SD are shown; n = 13.
