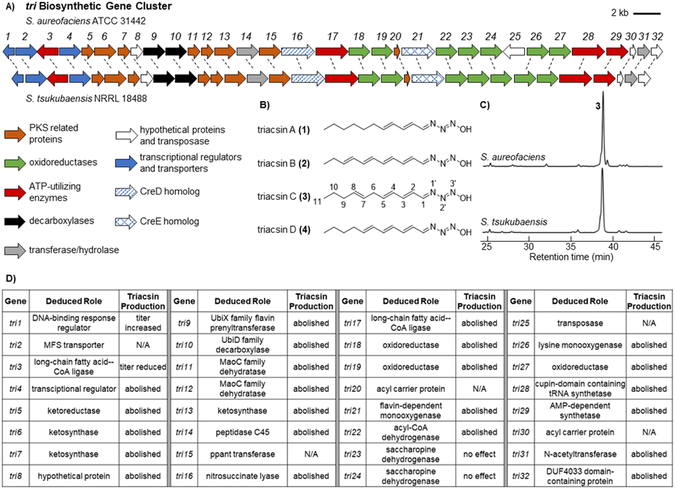
Figure 1.
Identification of the triacsin (tri) BGC and a previously unrecognized natural producer. A) Schematic of the tri BGC as discovered in S. aureofaciens and the homologous BGC identified in S. tsukubaensis. B) All four of the originally reported triacsin congeners contain an 11-carbon alkyl chain and the unique N-hydroxytriazene moiety. C) UV traces (300 nm) confirming the production of 3 in S. tsukubaensis. In both strains, the congener 3 was produced as the major product and other congeners were not identifiable by UV in these traces. D) Deduced roles of the tri genes based on sequence homology and summary of genetic results from the corresponding mutants. No mutants were generated for tri2, 15, 20, 25, and 30.