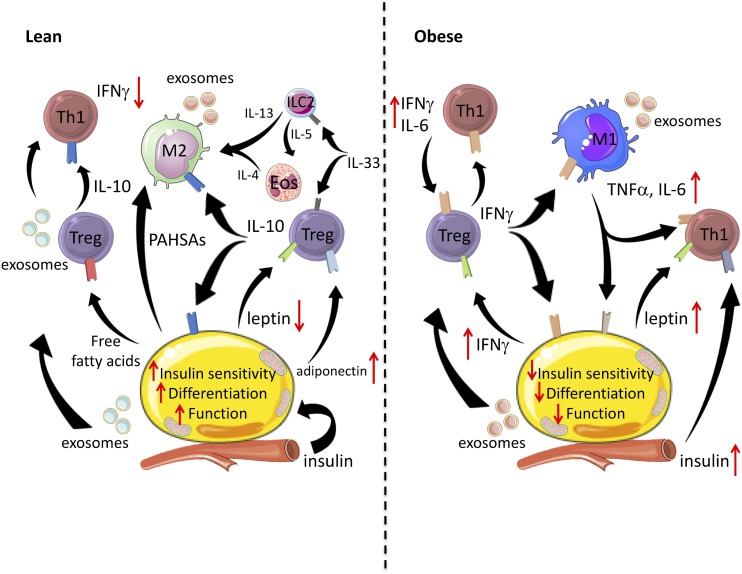
Figure 2.
Inter-cell crosstalk regulates metabolic and inflammatory functions in WAT. In lean WAT, insulin-sensitive adipocytes expand appropriately to anabolic pressure and secrete adipokines (adiponectin), FFAs and PAHSAs, and exosomes. Tregs produce IL-10 to suppress CD4+ Th1 T cell function, polarize M2 macrophages, and repress adipocyte-derived inflammatory cytokines. IL-33 derived from adipocytes and stromal cells activates Tregs and ILC2s. ILC2s recruit and activate esosinophils and, in combination, they produce type 2 cytokines that polarize M2 macrophages. Adipocytes secrete adiponectin and FFAs, which also suppress macrophage cytokine production and might influence Treg function, whereas the relative absence of leptin allows Tregs to proliferate and maintain suppressive activity. Both adipocytes and Tregs produce exosomes, with adipocyte-derived exosomes influencing macrophage differentiation and function, whereas Treg exosomes suppress T cells in some contexts. Lastly, lean adipocytes secrete fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids, such as PAHSAs, that regulate macrophages and peripheral insulin sensitivity. In summary, type 2 immune cells promote adipocyte insulin sensitivity, differentiation, and function through cytokines IL-4, IL-10, and M2 macrophage-derived exosomes. In obese adipose tissue, insulin resistance develops, and adipocyte differentiation is restricted, which contributes to ectopic lipid deposition. Adipocytes secrete inflammatory cytokines (IFNγ, TNFα, IL-6, RANTES, SAA) and recruit M1 macrophages (via MCP-1). Tregs, ILC2s, and eosinophils are reduced, with Tregs shifting toward IFNγ production. High levels of leptin and insulin also reduce Treg proliferation, function, and fatty acid metabolism. Obese adipocyte- or macrophage-derived exosomes also reduce insulin sensitivity. Collectively, accumulation of CD4+ Th1 T cells and M1 macrophages contributes to the increasing inflammatory milieu (IFNγ, TNFα, IL-6, and exosomes) that restricts adipocyte insulin sensitivity, expansion, and function.