Figure 6. ECs uptake extrinsic mitochondria that can co-localize with endogenous mitochondria.
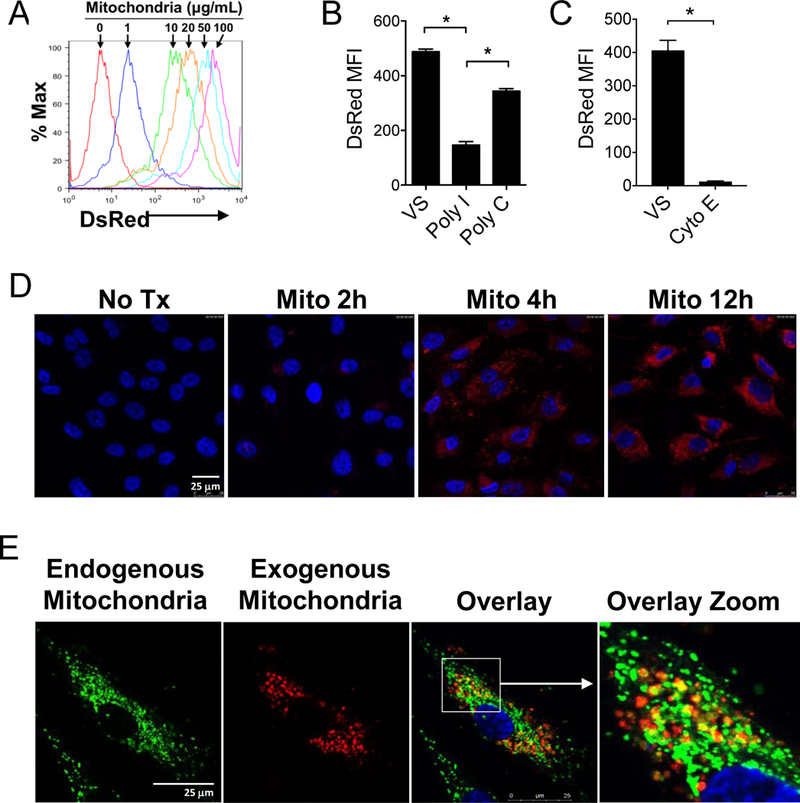
A) Confluent HAECs were incubated for 12 hr with DsRed-labeled human mitochondria at the indicated doses. B) poly-I (100 nM), a class A scavenger receptor inhibitor inhibited the uptake of DsRed-labeled mitochondria by ECs as determined by flow cytometry. Vehicle solution (VS) and Poly-C (100 nM) are negative controls. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. C) Cytochalasin E (10 mg/mL), an inhibitor of actin polymerization, also inhibited mitochondrial uptake. Comparisons were performed using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. *A p-value <0.05 was considered significant. D) Confocal microscopy of HAECs treated with 30 mg/mL DsRed-labeled mitochondria for increasing periods of time demonstrate intracellular localization of the exogenous mitochondria. Nuclei are labeled with DAPI nuclear stain (Blue). E) HAECs treated with MitoTracker Green to label endogenous mitochondria were then treated with exogenous DsRed-labeled mitochondria (30 μg/mL) for 6 hr. Co-localized endogenous and exogenous mitochondria are yellow in the overlay images.
