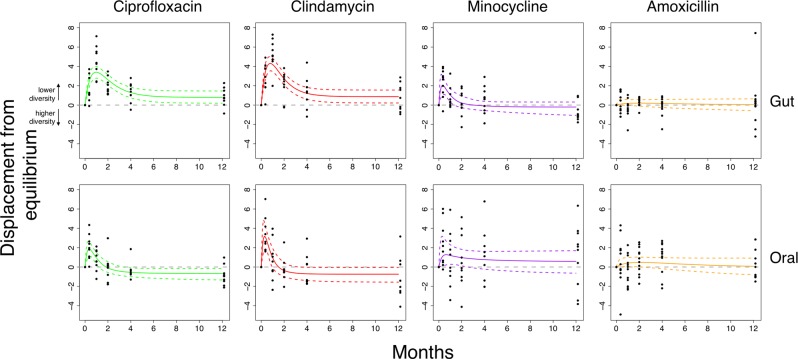
Fig. 3.
A model with a possible state transition is better supported for clindamycin and ciprofloxacin. Bayesian fits for participants taking either ciprofloxacin (green; n = 9), clindamycin (red; n = 9), minocycline (purple; n = 10), and amoxicillin (orange; n = 12). The mean phylogenetic diversity from 100 bootstraps for each sample (black points) and median and 95% credible interval from the posterior distribution (bold and dashed coloured lines, respectively). The grey line indicates the equilibrium diversity value, defined on a per-individual basis relative to the mean baseline diversity. The non-zero-centred asymptotes indicates support for a state transition in both the gut and oral microbiomes after ciprofloxacin and clindamycin. See Table 2 for Bayes Factors comparing model 2 to model 1