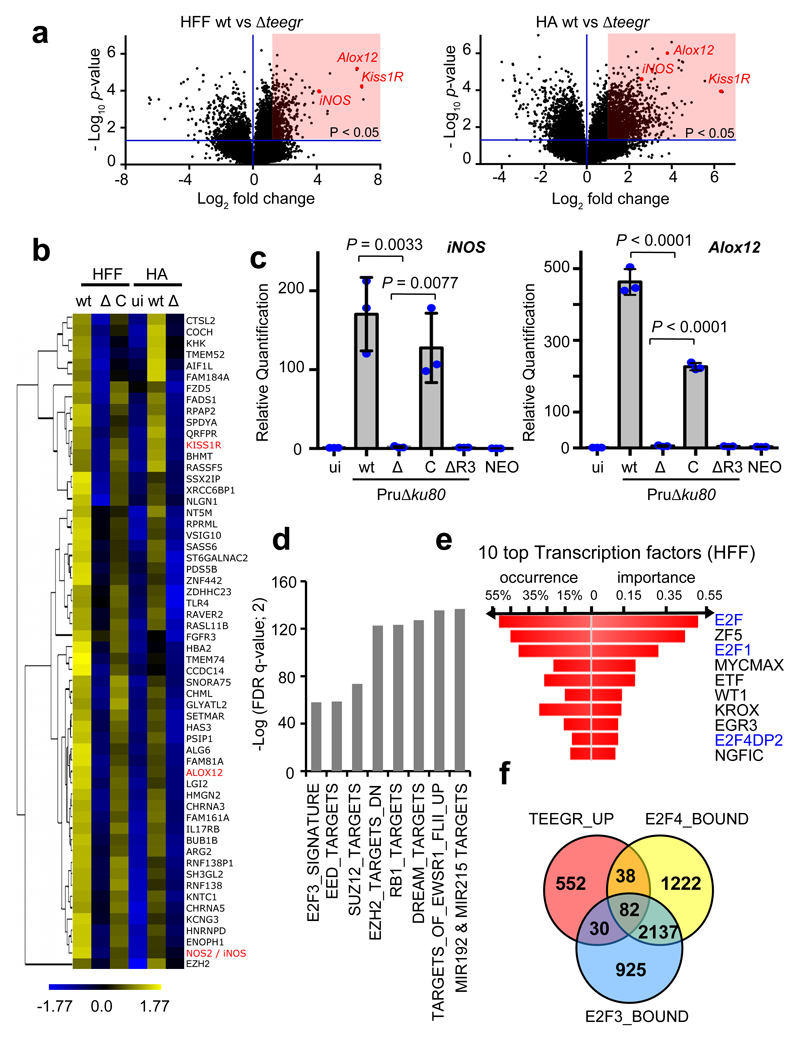
Fig. 2. TEEGR activates gene expression in human cells in a E2F3 and E2F4-dependent manner.
Genomewide expression profiling of human fibroblasts (HFF) and astrocytes (HA) infected with the ∆teegr mutant (∆), the parental type II strain Pru∆ku80 (wt) and the trans-complemented strain (C). a, Results of tests for differential expression are presented in a volcano plot which plots statistical significance against fold change for each gene. Genes (HFF, n=784; HA, n=1529, in red) with adjusted p-values (Bonferroni corrected P-value ≤ 0.05) and absolute fold changes of ≥1.5 are deemed of interest for in silico pathway analyses (Supplementary Table 1). b, Heat map of expression values for differentially expressed genes in human cells infected with WT, Δ and C parasites. For the 472 genes (more than fourfold, p < 0.05, unpaired t-test) that were defined as core TEEGR-regulated genes in HFF and HA, mean log2 gene expression values were median centered, genes were clustered by hierarchical clustering based on Pearson correlation, and a heat map with 58 genes is presented. The complete set of genes is listed in Supplementary Table 1. c, HFF cells were left uninfected (ui) or infected for 24 h with WT, Δ, C or TEEGR protein missing R3 (ΔR3). Levels of iNOS and Alox12 mRNAs were determined by RT-qPCR. Values were normalized to the amount of β2-microglobulin. Data are mean value ± SD of three biological replicates. The p-values were calculated using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. d, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) of the 784 genes positively regulated by TEEGR in HFF cells (Supplementary Table 1) highlighted eight gene expression signatures of chemical and genetic perturbations (CGP) that were significantly and selectively enriched (p < 0.05, False Discovery Rate (FDR)-corrected, two-sided Welch t-test). e, Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS) analysis of the 784 TEEGR-upregulated genes was performed by DIRE and the most significant transcription factors are listed. f, Venn diagram illustrating the overlap between the number of genes up-regulated by TEEGR (> twofold, p < 0.05, unpaired t-test) in HFF cells and the number of genes identified as E2F3- or E2F4-bound by Julian et al., (2016)39 and Marson et al., (2007)10 respectively.