Figure 2.
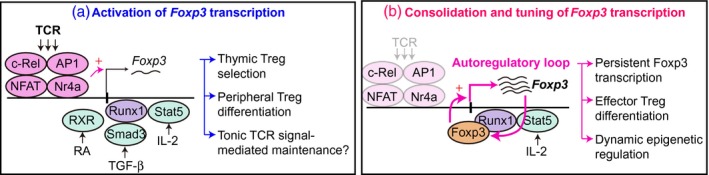
Activation versus consolidation and tuning of Foxp3 transcription. We propose to classify Foxp3 transcriptional regulation into two major mechanisms. (a) Activation of Foxp3 transcription is regulated mainly by T cell receptor (TCR) signals and enhanced by interleukin (IL)‐2, transforming growth factor (TGF)‐β and retinoic acid (RA). This may lead to thymic regulatory T cell (Treg) selection and peripheral Treg differentiation. In addition, tonic TCR signals through self‐reactive TCRs may use this mechanism to regulate homeostatic Foxp3 transcription. (b) Consolidation and tuning of Foxp3 transcription. The maintenance of Foxp3 transcription requires CNS2 of the Foxp3 gene, which may provide a platform for Foxp3–Runx1/CBF‐β complex to form the autoregulatory transcriptional circuit (autoregulatory loop) for the Foxp3 gene. The activity of this loop can be affected by IL‐2 signalling via phosphorylated signal tranducer and activator of transcription‐5 (STAT)‐5. This mechanism may lead to temporally persistent Foxp3 transcription, which promotes effector Treg differentiation, and the dynamic regulation of epigenetic modifications during Treg differentiation.
