Figure 5.
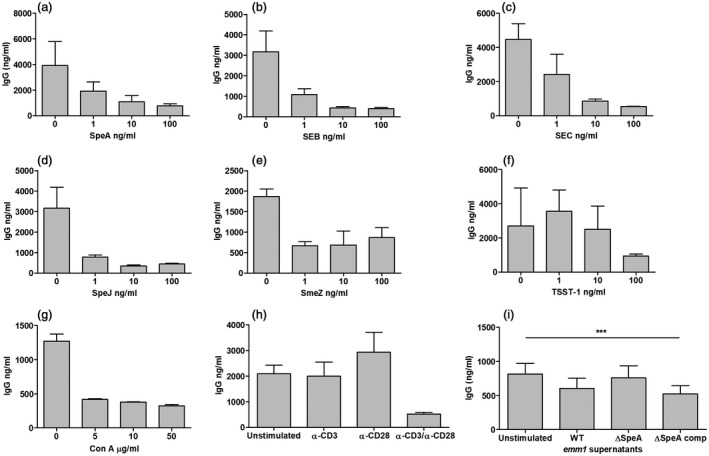
Immunoglobulin (Ig)G production by tonsil cell suspensions is reduced by superantigens and T cell mitogens. IgG release in the presence of different concentrations of bacterial superantigens was tested at 1 week: streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin (SpeA) (a), staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) (b), staphylococcal enterotoxin C (SEC) (c), streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin J (SpeJ) (d), streptococcal mitogenic exotoxin Z (SmeZ) and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST‐1) (f). For comparison, the T cell mitogen concanavalin (Con) A was tested (g) and T cell stimulation using anti(α‐)CD3 and CD28 antibodies (h). Mean and standard deviation (s.d.) of experimental triplicates from one representative tonsil donor (data representative of experiments using three donors for the different superantigens, two for concanavalin A and α‐CD3/28. IgG release was measured from cells cultured in the presence of emm1 S. pyogenes culture supernatants differing only in SpeA production (i). Supernatants containing SpeA [wild‐type (WT) and SpeA‐complemented, ΔspeAcomp] reduced IgG production, in contrast to supernatant from a SpeA gene deletion mutant (ΔspeA). Mean and standard deviation (s.d.) of five donor tonsils shown, P < 0·0001*** (two‐way analysis of variance (anova)].
