Figure 2.
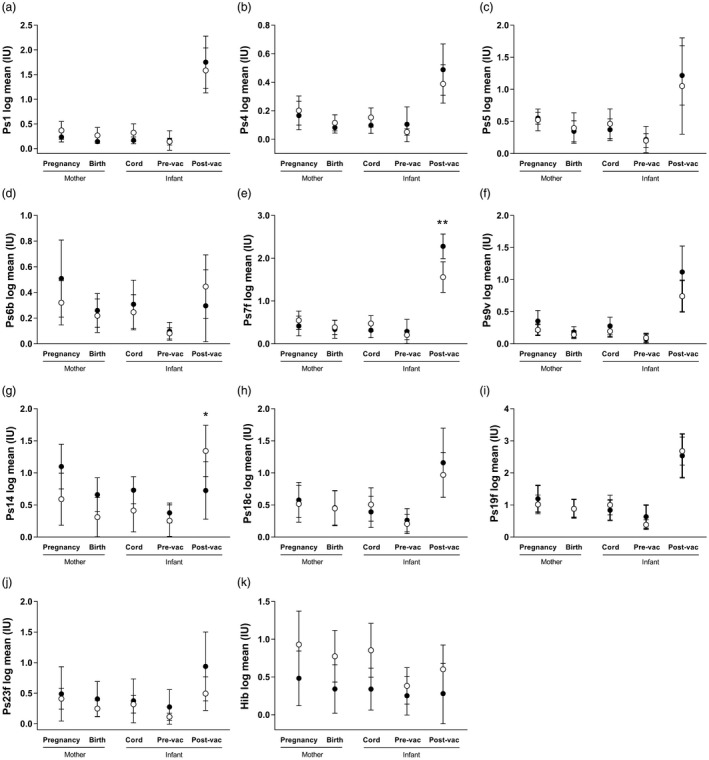
Longitudinal pneumococcal and Haemophilus influenzae (Hib) antibody concentrations in mothers and their infants from maternal tetanus, diphtheria and acellular pertussis (Tdap) vaccinated and unvaccinated pregnancies. Immunoglobulin (Ig)G against pneumococcal serotypes (Ps) and Hib were quantified in mother–infant pairs from vaccinated (white circles) and unvaccinated (black circles) pregnancies. Data were log‐transformed, and a random‐effects model applied. Mean and 95% confidence intervals are shown. No differences were observed in antibody to serotypes (a) 1, (b) 4, (c) 5, (d) 6B, (e) 7F, (f) 9V, (g) 14, (h) 18C, (i) 19F, (j) 23F in mothers during pregnancy and at birth, or in cord blood and the infant prevaccination (pre‐vac; 7 weeks of age). Post‐vaccination (post‐vac; 5 months of age), infants from vaccinated pregnancies had elevated serotype 14, whereas infants from the unvaccinated group had elevated 7F. (k) Hib antibody did not differ between vaccinated and unvaccinated groups at any study time‐points (*P < 0·05; **P < 0·01; unvaccinated n = 15; vaccinated n = 16).
