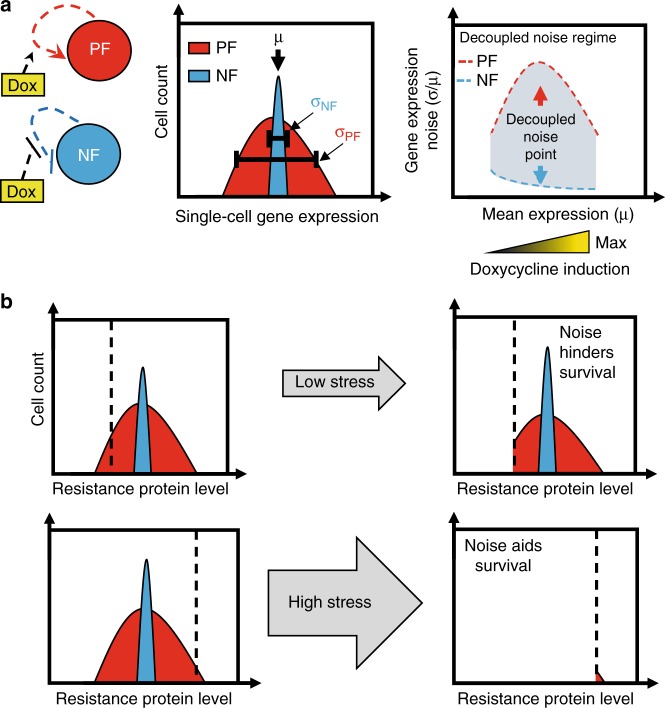
Fig. 1.
Stress-dependent effect of network noise on drug resistance. a Tuning the induction (yellow gradient) of mammalian positive (mPF, left, red circle) or negative (mNF, left, blue circle) feedback synthetic gene circuits can confer high and low gene expression noise while the mean expression is identical. This enables decoupling gene expression noise amplitude (middle, standard deviation divided by the mean; σ/μ) from the mean within a decoupled noise regime (right, red and blue dashed lines) composed of decoupled noise points (right, red and blue arrows). b Schematic depictions to illustrate fractional viability under low or high levels of drug (stress, grey arrow) for cells with high (red distribution) or low (blue distribution) gene expression noise of a drug resistance gene. Relative survival of cells upon drug treatment will depend on network noise relative to the fitness function (dashed black line). If the fitness function is steep, noise hinders survival under low levels of drug while it is beneficial under high levels of drug (Supplementary Fig. 1)