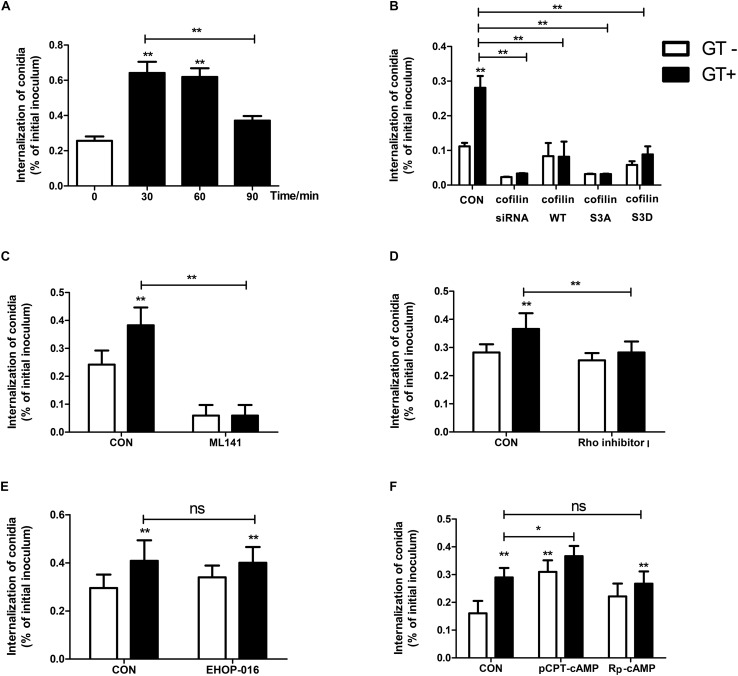
FIGURE 5.
Cdc42, RhoA, and cAMP/PKA modulate gliotoxin-induced internalization of A. fumigatus into lung epithelial cells. Prior to inoculation with A. fumigatus conidia, A549 cells were treated with gliotoxin for the indicated periods (A), or transfected with siRNA targeting cofilin or plasmid encoding wild-type cofilin, cofilin S3A, or cofilin S3D plasmids (B), or pretreated with 50 μM ML141 (Cdc42 inhibitor) (C), or pretreated with 0.5 μg/ml Rho inhibitor I (RhoA inhibitor) for 1 h (D), or pretreated with 2 μM EHOP-016 (Rac1 inhibitor) for 24 h (E), or pretreated with 100 μM pCPT-cAMP (PKA agonist) or 100 μM Rp-cAMP (PKA antagonist) for 30 min (F), followed by gliotoxin treatment for 30 min. All cells were inoculated with A. fumigatus conidia at a MOI of 20 for 6 h. The internalization was assessed by the nystatin protection method. Experiments were performed in three independent experiments with three individual replicates. Statistically significant differences were determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test or by Dunnett post hoc test. *p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.