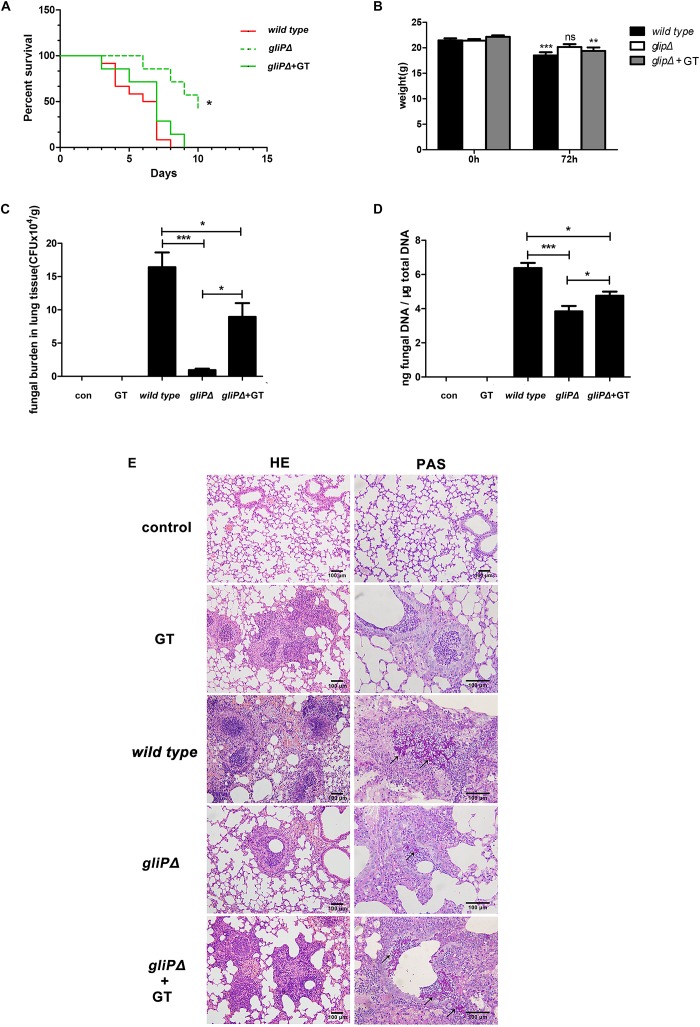
FIGURE 6.
Exogenous gliotoxin promotes invasion of A. fumigatus into lung tissue in a mouse model of invasive aspergillosis. C57BL/6 mice were immunosuppressed with hydrocortisone acetate and inoculated intranasally with conidia of A. fumigatus wild-type B5233, gliPΔ, or gliPΔ plus exogenous 50 ng/ml gliotoxin. For survival analysis (A) and weight change analysis (B), mice were weighed every 24 h from the day of infection and were visually inspected twice daily. Mice were sacrificed at 72 h post-infection to measure the fungal burden in the lung tissue by counting CFUs (C) or by RT-PCR method (D). (E) Lung tissues were stained with HE and PAS, and observed by light microscopy (Olympus BX51) at a magnification of 200× or 400×. Black arrows indicate hyphae (red). Experiments were performed in three independent experiments with three individual replicates. Statistically significant differences were determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test. *p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. Statistically significant difference were determined using unpaired Student’s t-tests with a 95% confidence interval, using GraphPad Prism software. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.