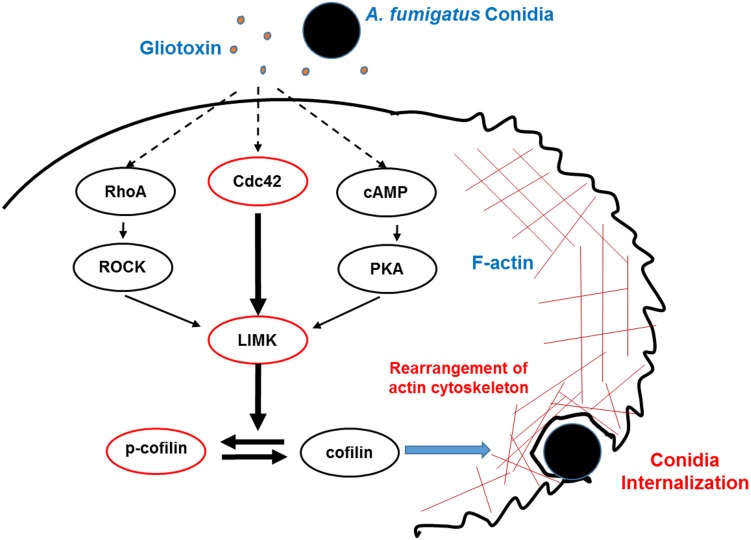
FIGURE 7.
Model of phosphorylation of cofilin and actin cytoskeleton rearrangement induced by gliotoxin during A. fumigatus internalization into lung epithelial cells. During the interaction between A. fumigatus conidia and lung epithelial cells, gliotoxin, at a rather low concentration, might induce cofilin phosphorylation mainly through Cdc42 signaling, and in addition, through RhoA activation and increases in cAMP and PKA activation, which all lead to LIMK1 activation and phosphorylation of cofilin, which subsequently modulates actin cytoskeleton rearrangement and facilitates the internalization of conidia into host cells. Dashed lines indicate signal pathway interactions hypothesized to occur in A549 cells.