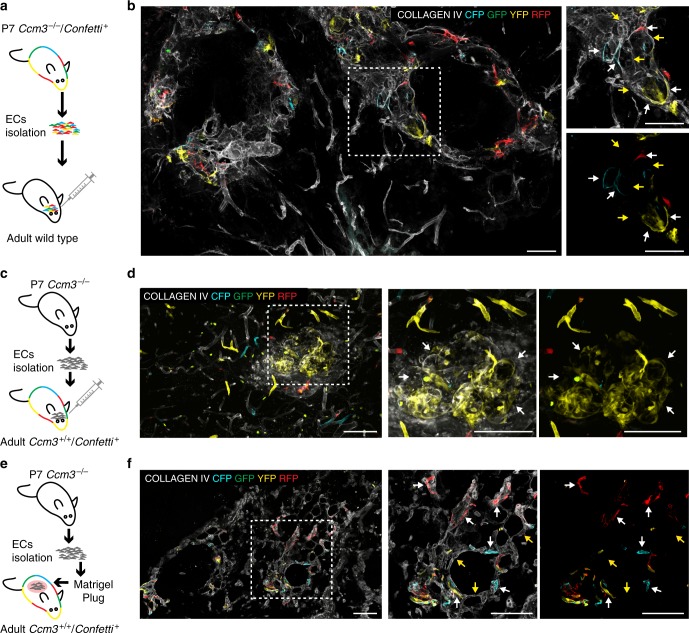
Fig. 6.
Ccm3−/− cells form cavernomas and recruit Ccm3+/+ cells in wild-type animals. a Endothelial cells were isolated from acute Cdh5(PAC)-Cre-ERT2/Ccm3fl/fl/R26R-Confetti at P7 and re-injected into the brains of adult wild-type mice. b Brain section showing the formation of aberrant vessels that comprise both Confetti-positive endothelial cells, which are Ccm3−/− coming from the donor, as well as non-labelled Ccm3+/+ endothelial cells coming from the host. c In the same way, endothelial cells were isolated from acute Cdh5(PAC)-Cre-ERT2/Ccm3fl/fl at P7 and re-injected into the brains of adult Cdh5(PAC)-Cre-ERT2/R26R-Confetti mice treated with 2 mg of Tamoxifen 1 week before injection. d Brain section showing the formation of aberrant vessels, which comprise also Ccm3+/+ Confetti-positive endothelial cells coming from the host. e Endothelial cells were isolated from acute Cdh5(PAC)-Cre-ERT2/Ccm3fl/fl at P7 and engrafted in a subcutaneous Matrigel plug into adult Cdh5(PAC)-Cre-ERT2/R26R-Confetti mice. f Section of the plug showing the formation of aberrant vessels, which comprise both non-labelled Ccm3−/− endothelial cells coming from the donor as well as Confetti-positive endothelial cells, thus Ccm3+/+ coming from the host. White arrows, endothelial cells positive for Confetti; yellow arrows, endothelial cells negative for Confetti. Scale bars, 100 μm