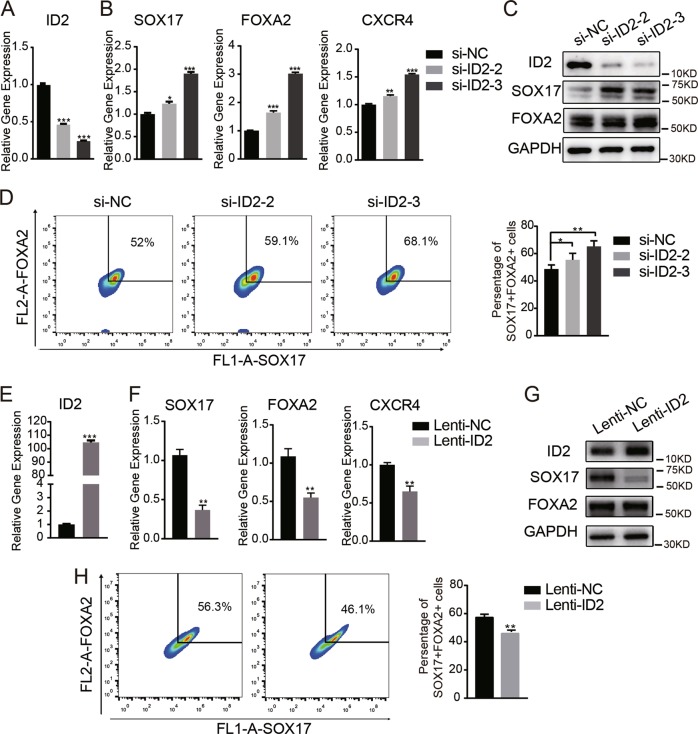
Fig. 5. ID2 negatively regulates the differentiation of hAMSCs to DE.
a ID2 was silenced in hAMSCs using two independent siRNAs (si-ID2-2 and si-ID2-3). The knockdown efficiency was verified by qRT-PCR compared with the negative control (NC). b qRT-PCR analysis detected DE marker genes (SOX17, FOXA2, and CXCR4) in ID2-knockdown hAMSCs and control hAMSCs on day 5 after DE induction. c Western blot detected the expression of ID2, SOX17, and FOXA2 in ID2-knockdown hAMSCs and control hAMSCs on day 5 after DE induction. d Flow cytometry analysis of the FOXA2+/SOX17+ subpopulation in si-ID2 hAMSC or si-NC hAMSCs on day 5 after DE induction. e hAMSCs were transduced with lentivirus overexpressing ID2 (Lenti-ID2) or empty vectors (Lenti-NC). The efficiency of ectopic expression was verified by qRT-PCR. f qRT-PCR analysis detected DE marker genes (SOX17, FOXA2, and CXCR4) in Lenti-ID2 hAMSCs or Lenti-NC hAMSCs on day 5 after DE induction. g Western blot detected the expression of ID2, SOX17, and FOXA2 in Lenti-ID2 hAMSCs or Lenti-NC hAMSCs on day 5 after DE induction. h Flow cytometry analysis of the FOXA2+/SOX17+ subpopulation in lenti-ID2 hAMSCs or Lenti-NC hAMSCs on day 5 after DE induction. Data are shown as the means ± S.D. (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001