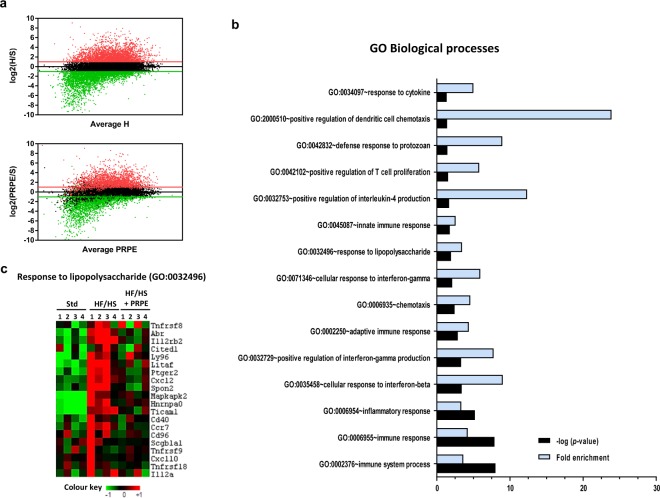
Figure 7.
HF/HS diet supplementation with PRPE normalizes HF/HS-induced changes in the expression of genes associated with immune-inflammatory processes. (a) High-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was performed on mRNA samples isolated from the eWAT of mice fed the Std (n = 4), HF/HS (n = 4) or HF/HS + PRPE (n = 4) diet for 180 days. The results are presented as fragments per kilobase of exon per million fragments mapped (FKPM (log2 values), fold changes compared to the Std (S) group) and were plotted against the average FKPM for the HF/HS (H) or HF/HS + PRPE group (PRPE). Green and red lines indicate the cutoff value for fold changes (≥2) and for differential expression (FDR < 0.05). Upper panel: Genes that were upregulated or downregulated by at least 2-fold by the HF/HS diet compared to the standard chow (Std) are labelled in red and green, respectively. Genes with similar expression are labelled in black. Lower panel: Among the 7713 genes that were significantly upregulated by the HF/HS diet (fold changes ≥2), 709 genes were significantly downregulated by PRPE supplementation. (b) Gene ontology analysis was performed on genes that were significantly upregulated by the HF/HS diet and significantly downregulated by PRPE supplementation. The top 15 GO biological processes are shown, along with the –log(p-value) and fold enrichment of significant terms. (c) Cluster of genes involved in the lipopolysaccharide response (GO: 0032496). Data are presented as FKPM values.