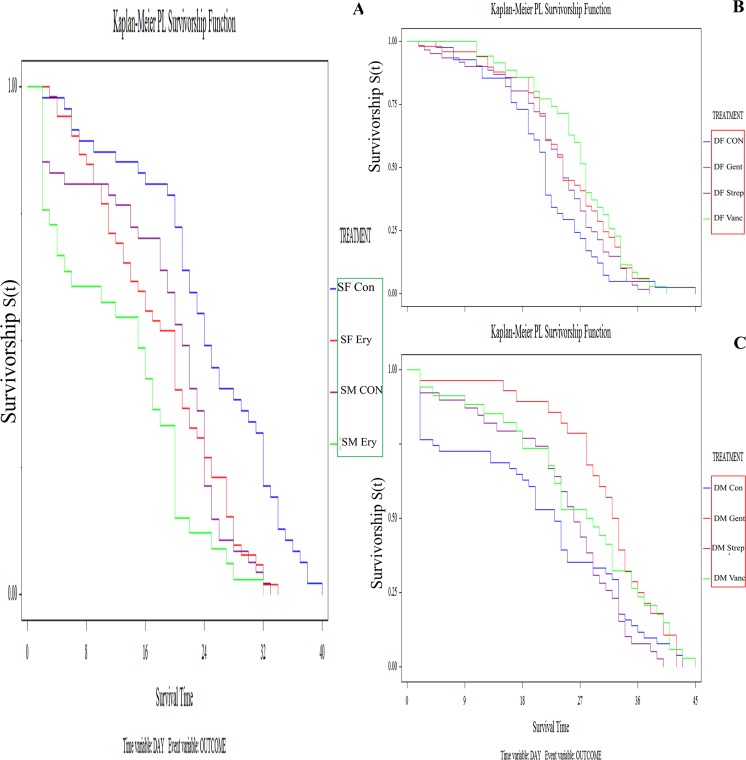
Figure 1.
The effect of antibiotic supplementation on Anopheles arabiensis longevity. (A) For the insecticide-susceptible Anopheles arabiensis SENN strain control treatments (SFCon-dark blue and SMCon-purple) lived significantly longer than erythromycin-treated individuals (SFEry-red and SMEry-green). (B) Untreated control females of the Anopheles arabiensis insecticide-resistant SENN-DDT strain (DFCon-dark blue) lived for a significantly shorter time than gentamicin- (DFGent-red), vancomycin- (DFVan-green), or streptomycin-treated individuals (DFStrep-purple). Vancomycin treated females lived the longest. (C) Untreated control males of the Anopheles arabiensis insecticide-resistant SENN-DDT strain (DMCon-dark blue) lived for a significantly shorter time than gentamicin- (DMGent-red), vancomycin- (DMVan-green), or streptomycin-treated individuals (DMStrep-purple). Gentamicin-treated males lived the longest. Significance was determined by the Log-Rank test. Insecticide susceptible strains are denoted by a green block and insecticide resistant strains are denoted by a red block.