Figure 2.
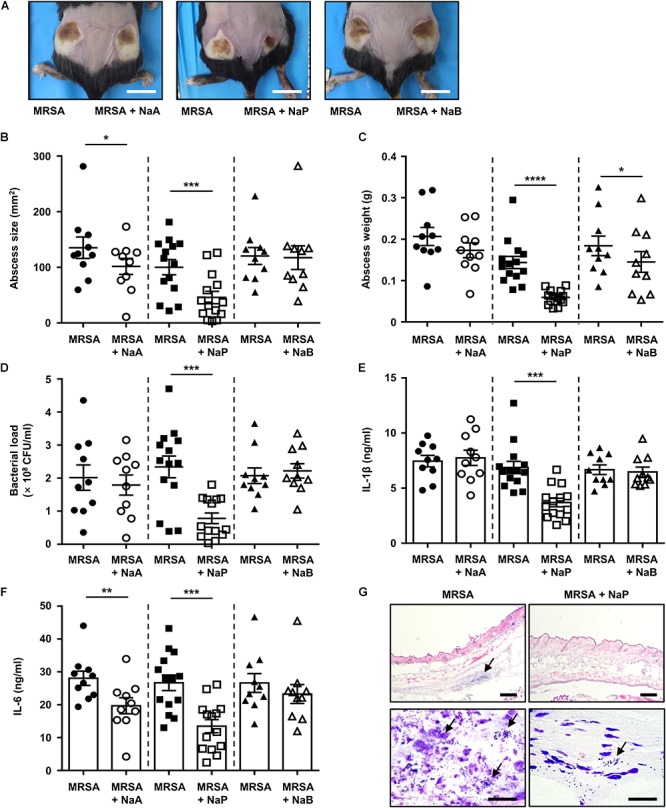
NaP reduces bacterial load and dermonecrosis in murine MRSA skin infection. C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously infected with 3 × 106 CFU MRSA USA300 alone (left), or together with 50 mM NaA, NaP, or NaB (right) (n = 10–14 per group). (A) Images of abscesses on day 3. Scale bars indicate 1 cm. On day 3, after euthanasia of mice, (B) size and (C) weight of abscesses were measured. (D) Bacterial load was measured by excising and homogenizing abscesses aseptically, and spotting homogenates on TSB agar plates. Homogenates were centrifuged and the supernatants were used to measure (E) IL-1β and (F) IL-6. (G) Abscesses were cryosectioned and evaluated for histopathology by H&E staining and Gram staining. Scale bars indicate 200 and 20 μm for top and bottom panels, respectively. Data are represented as mean values ± SEM, and statistical significance was measured with the student’s t-test. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001.
