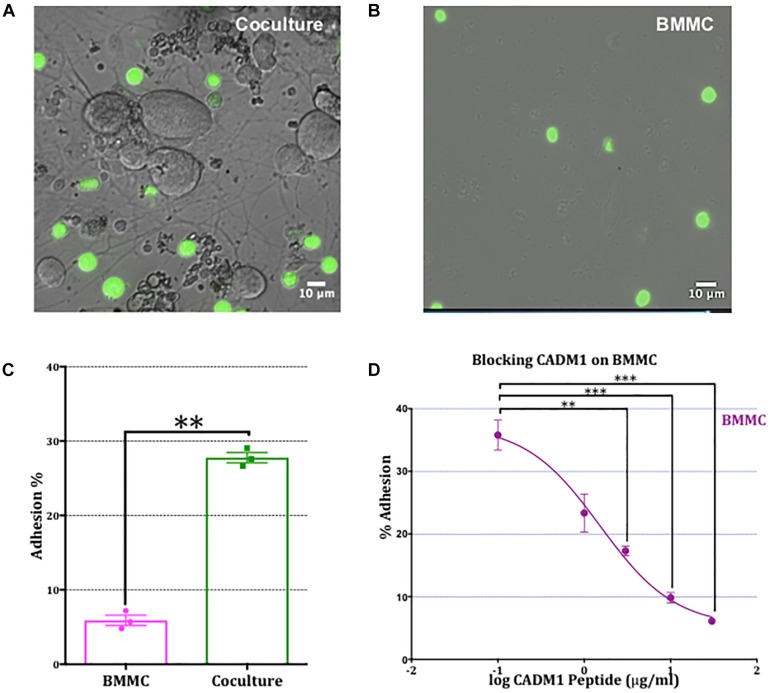
FIGURE 3.
Adhesion of mast cells to sensory neurons is attenuated by a CADM1 blocking peptide. (A) Superimposed bright-field and fluorescent image of live calcein-labeled, adherent BMMCs (green) co-cultured with DRG neurons (unlabeled cells) for 2 h. Non-adherent cells have been removed by washing and centrifugation of the plate. (B) Image of calcein-labeled BMMCs plated in parallel into matrigel-coated wells devoid of neurons and subjected to the same washing and centrifugation procedure. (C) BMMC adhesion quantified from calcein-fluorescence remaining in wells after washing and centrifugation expressed as a percentage of total well fluorescence measured prior to washing procedure. Data shown as mean ± SEM from N = 3. Each done in duplicate. Data were analyzed using a two-tailed paired t-test ∗∗p < 0.01. (D) Concentration-dependent inhibition of mast cell adhesion to DRG measured with a CADM1 blocking peptide. Percentage of adherent BMMC was calculated using the calcein adhesion assay. Each condition was done in duplicate, on N = 3 cultures. Each point represents the mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Turkey’s multiple comparison post-test was performed. ∗∗ denotes p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗ p < 0.001 compared to the percentage of BMMC adhesion in the absence of CADM1 blocking peptide.