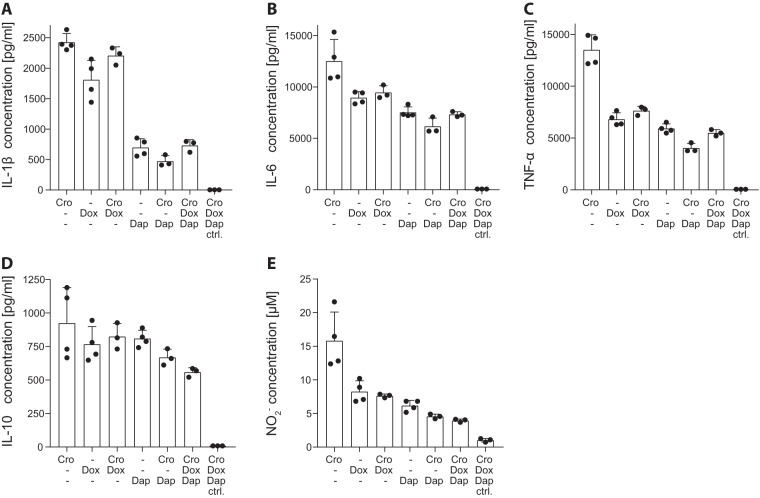
FIG 1.
Inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide (NO) production upon in vitro stimulation of astroglial cells with living S. pneumoniae bacteria. Cytokines and NO were measured in cell culture supernatant 24 h after concomitant application of living S. pneumoniae bacteria and antibiotics. Infection and bacteriolysis induced by ceftriaxone (CRO) resulted in high levels of IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B), TNF-α (D), and NO (E) release. Compared to CRO monotherapy, DOX significantly reduced levels of IL-1β (P < 0.002), IL-6 (P < 0.002), TNF-α (P < 0.0001), and NO (P < 0.001); CRO+DOX significantly decreased levels of IL-6 (P < 0.02), TNF-α (P < 0.0001), and NO (P < 0.001); DAP, CRO+DAP, and CRO+DAP+DOX reduced levels of IL-1β (P < 0.0001), IL-6 (P < 0.0001), TNF-α (P < 0.0001), and NO (P < 0.0001). CRO+DAP+DOX was the only regimen to significantly reduce IL-10 levels (P < 0.03). Significance levels are not indicated in the graphs for clearer representation. Statistical differences were assessed by one-way ANOVA using Tukey’s multiple comparison to adjust for multiple testing.