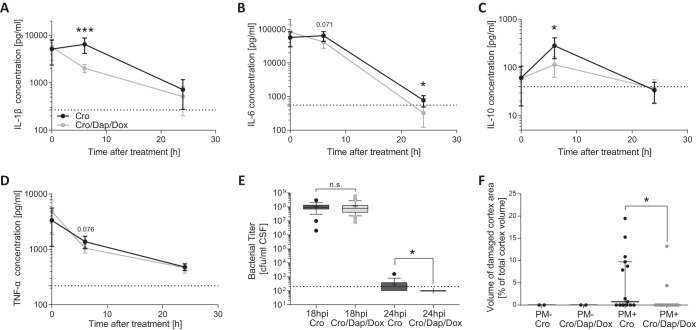
FIG 3.
Inflammatory CSF cytokine levels, cortical necrosis, and bacterial clearance from CSF during acute PM. Cytokine levels are represented by means ±95% confidence intervals starting before treatment initiation and at 6 h and 24 h after treatment start (representing 18, 24, and 42 hpi) for IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B), IL-10 (C), and TNF-α (D). Combination adjuvant therapy (n = 11) significantly reduced IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10 CSF levels compared to those with CRO monotherapy (n = 11) while showing a trend toward a reduced TNF-α CSF level 6 h after treatment start. Bacterial titers in the CSF were similar in the two treatment groups before the start of therapy (at 18 hpi; n = 53 for CRO+DAP+DOX; n = 49 for CRO), with a faster bacterial clearance in animals receiving the combined-adjuvant therapy (n = 17) than that with CRO monotherapy (n = 18) (E). Cortical necrosis was found only in animals with PM and was significantly reduced by combined-adjuvant therapy (n = 15) compared to the level with CRO monotherapy (n = 15) (F). Statistical differences were assessed using an unpaired t test for cytokines and bacterial titer at 18 hpi. For necrotic cortex volume and bacterial titer at 24 hpi, a Mann-Whitney test was used as data were not normally distributed. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant.