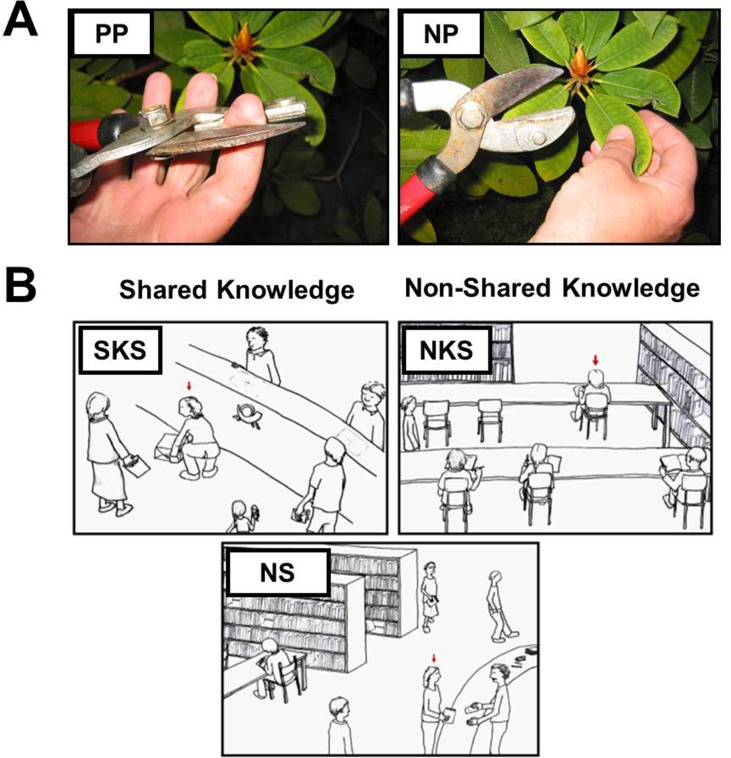
Figure 1.
Stimuli used in the functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)experiments. (A) Depiction of one example stimulus of the experimental paradigm to induce empathy for physical pain. The physical pain situation (PP) is presented on the left and the neutral, no-pain control situation on the right side [NP; stimuli were taken from Jackson et al. (36)]. (B) The situations eliciting empathy for social pain varied concerning the social target’s awareness about the inappropriateness of the situation and thus regarding the shared knowledge and affective experience of the observer and the social target. Ten situations depicted situations with shared knowledge about the inappropriateness of the situation (SKS) eliciting shared affect with the social target, e.g., sharing embarrassment with a person who’s pants rip while she bends down to lift a package, and 10 situations depicted a social target unaware about the faux pas, thus not sharing the same knowledge with the observer [non-shared knowledge situation (NKS)], e.g., a person whose pants unknowingly slipped down while she is sitting on a chair. Ten sketches displayed non-norm-violating control situations [neutral control situations (NS)]. Stimuli were presented together with two sentences describing the situation below the sketches (e.g., You are at a library: you observe a women giving back a book she borrowed).