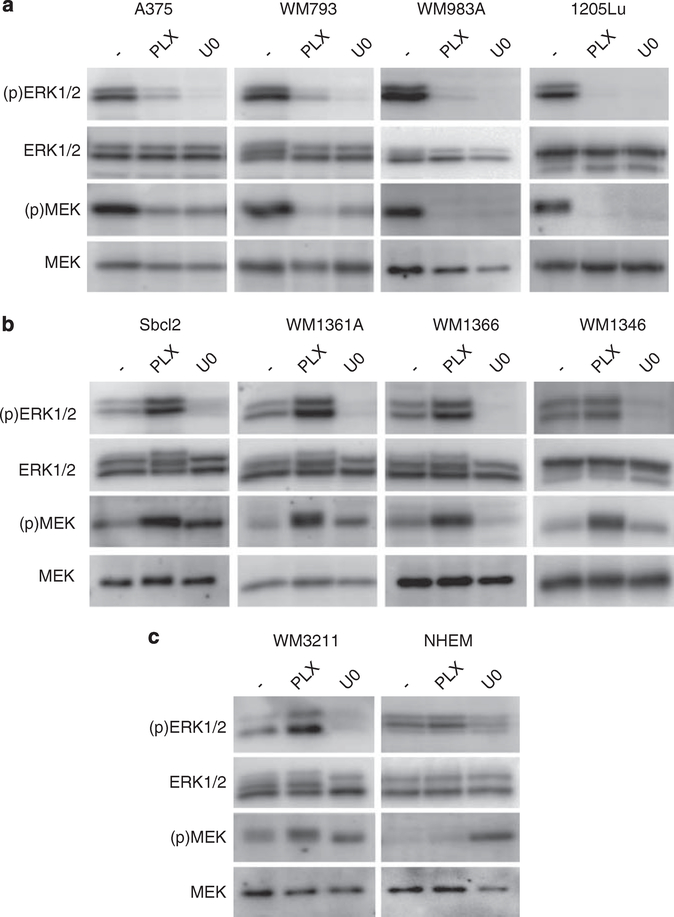
Figure 1.
Treatment of mutant N-RAS melanoma cell lines induces MEK-ERK1/2 signaling. (a) Mutant B-RAF cell lines A375, WM793, WM983A and 1205Lu (all B-RAFV600E); (b) Mutant N-RAS cell lines Sbcl2, WM1361A, WM1366 and WM1346; and (c) wild-type B-RAF/N-RAS WM3211 cells and neonatal human melanocytes (NHEM) were cultured, as previously described (Satyamoorthy et al., 1997; Conner et al., 2003; Tsai et al., 2008). All cell lines were treated with DMSO (−), 1 μM PLX4720 (PLX) (Plexxikon) and 10 μM U0126 (U0) (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) for 16 h. Lysates were analyzed by western blotting as previously described using a Versadoc Imaging system (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) (Boisvert-Adamo and Aplin, 2006). Antibodies for ERK1/2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA); MEK1, phospho-ERK (Thr202/Tyr204) ((p)ERK1/2), phospho-MEK1/2 (Ser217/Ser221) ((p)MEK) (Cell Signaling Technology).