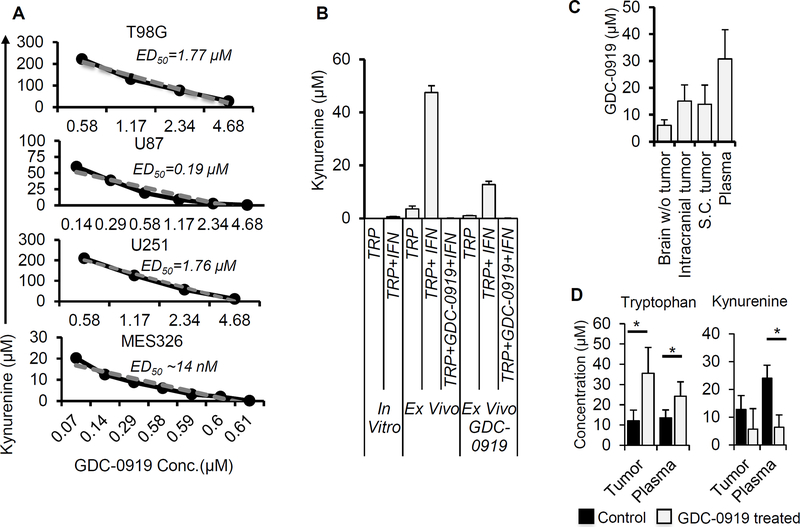
Figure 3. GDC-0919 demonstrates potent inhibition of tryptophan metabolism in glioblastoma and achieves biologically relevant concentrations in the brain.
(A) Human GBM cell lines (T98G, U87, U251 and MES326) were cultured with human IFN-γ (50 ng/ml) and of tryptophan (250 μM) and graded concentrations of the IDO1 inhibitor GDC-0919. The supernatant was collected after three days and evaluated for kynurenine. Data was plotted and used to calculate ED50 values for individual cell lines. (B) Murine TRP tumors (in vitro and ex vivo tumors isolated from C57BL/6 mice and C57BL/6 mice treated with GDC-0919 (200 mg/kg twice a day for 3 days given orally) were cultured in the presence and absence of mouse IFN-γ (100 ng/ml) and tryptophan (250 μM). The supernatant was collected after three days and analyzed for kynurenine. (C/D) C57BL/6 mice with subcutaneous or intracranial TRP tumors were treated with GDC-0919 (200 mg/kg twice a day for 3 days given orally). Tissue and plasma were isolated after three days of treatment and analyzed for (C) GDC-0919 and (D) tryptophan and kynurenine (in intracranial tumors) using LC/MS. Results obtained in mg/kg were converted to μM by assuming mg/ml ratio to be 1. Data represent mean ± SD. *= p<0.05. A minimum of 4 tissue samples were used for each experiment.