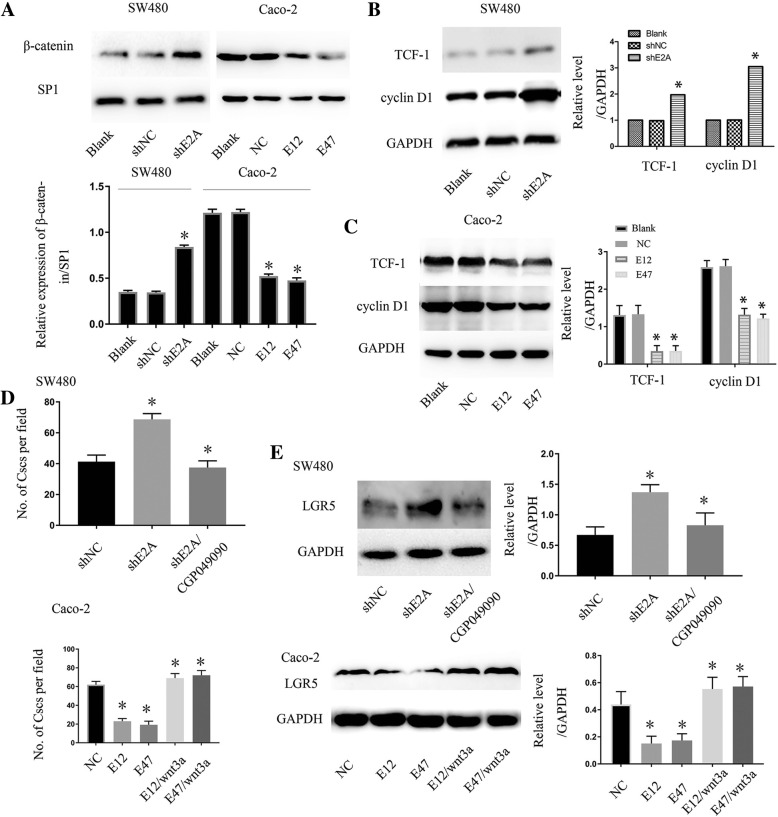
Fig. 4.
Wnt/β-catenin pathway is crucial for E2A in CRC cell tumor-initiating capacity. a Effect of E2A on the expression of β-catenin in cell nuclei. shE2A expression enhanced the β-catenin expression in SW480 cell nuclei, and E12/E47 attenuated the β-catenin expression in Caco-2 cell nuclei. Lower panel: Densitometric analysis of beta-catenin normalized to SP1. Data in the histograms is expressed as means ± SD from three separate experiments. b, c E2A suppressed the Wnt pathway in CRC cells. shE2A increased expression of the Wnt pathway effectors TCF-1 and cyclin D1 in SW480 cells, whereas E12 and E47 had the opposite effect in Caco-2 cells. Right panel: Densitometric analysis of TCF-1 and cyclin D1 normalized to GAPDH. Data in the histograms is expressed as mean ± SD from three separate experiments. d Wnt pathway is crucial for E2A suppressing tumor-initiating ability. SW480/shE2A cells treated with 5 μM CGP049090, which is a small-molecular compound inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway activity, had decreased tumor-initiating ability compared with that of SW480/shE2A without CGP049090 (upper panel). wnt3a, at 100 ng/mL, added Caco-2 restored the tumor-initiating ability inhibited by E12/E47 to a level like that in Caco-2/NC cells (lower panel). e Lgr5 expression in SW480/shE2A cells treated with 5 μM CGP049090 was like that in SW480/shNC, which was lower than that in SW480/shE2A without CGP049090. wnt3a, at 100 ng/mL, added to Caco-2 cells, restored the Lgr5 expression inhibited by E12/E47 to a level like that in Caco-2/NC cells (lower panel). Data are the mean ± SD from at least three separate experiments. *, P < 0.05