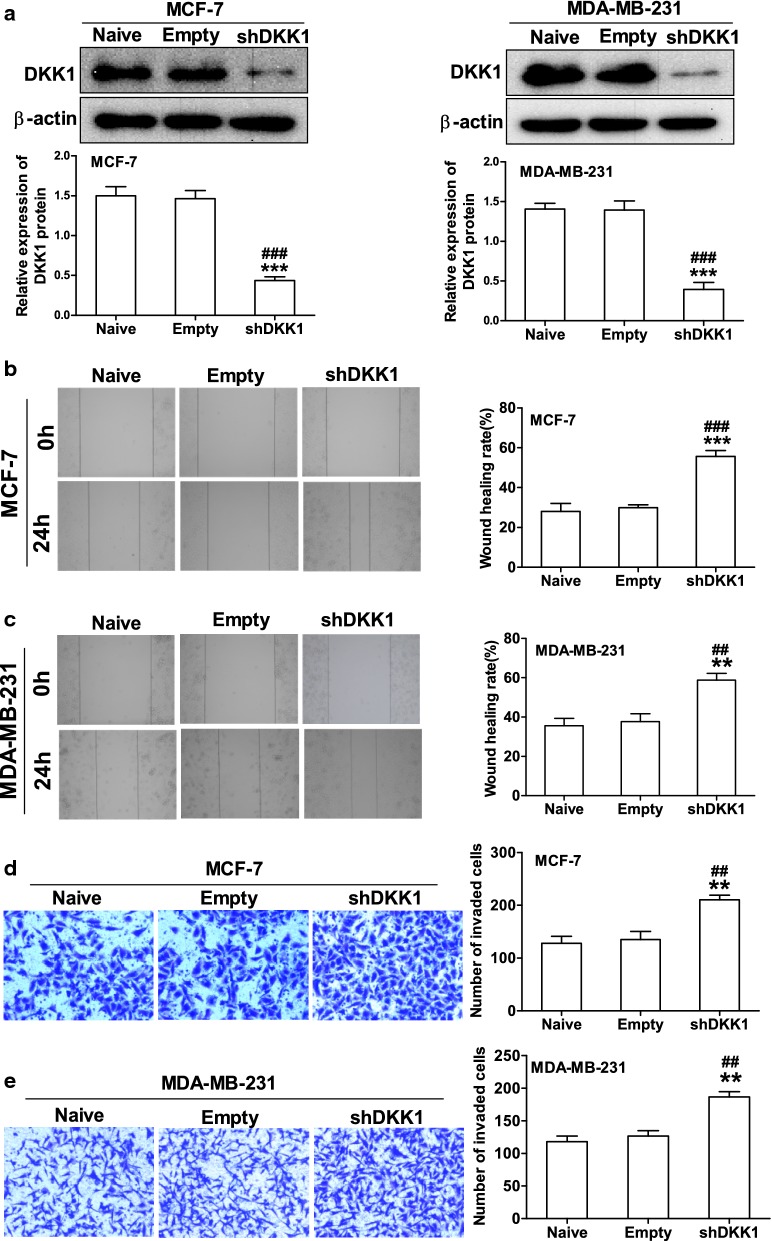
Fig. 3.
Knockdown of DKK1 enhanced the ability of migration and invasion in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. a Western blot of DKK1 protein expression in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells after transfected with empty vector or DKK1 shRNA. Note that DKK1 was knocked down in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells after transfected DKK1 shRNA. ***p < 0.001 compared to the empty vector group, ###p < 0.001 compared to the naive group, n = 5 per group, one-way ANOVA. Naïve: untreated group, Empty: empty vector group, shDKK1: DKK1 knockdown group. Wound scratch assay showed knockdown of DKK1 enhanced cell migration in MCF-7 (b) and MDA-MB-231 (c) cells. Left: representative images of wound scratch. Right: histograms represent the analysis of the wound healing rate. Results are presented as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the empty vector group, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, n = 5 per group, one-way ANOVA. Naïve: untreated group, Empty: empty vector group, shDKK1: DKK1 knockdown group. Transwell chamber coated with Matrigel assay suggested knockdown of DKK1 increased the cell number invaded through Matrigel in MCF-7 (d) and MDA-MB-231 cells (e). Left: representative images of transwell assay. Right: histograms represent the analysis of the number of invaded cells. Results are presented as mean ± SEM, **p < 0.01 compared to the empty vector group, ##p < 0.01 compared to the naive group, n = 5 per group, one-way ANOVA. Naïve: untreated group, Empty: empty vector group, shDKK1: DKK1 knockdown group