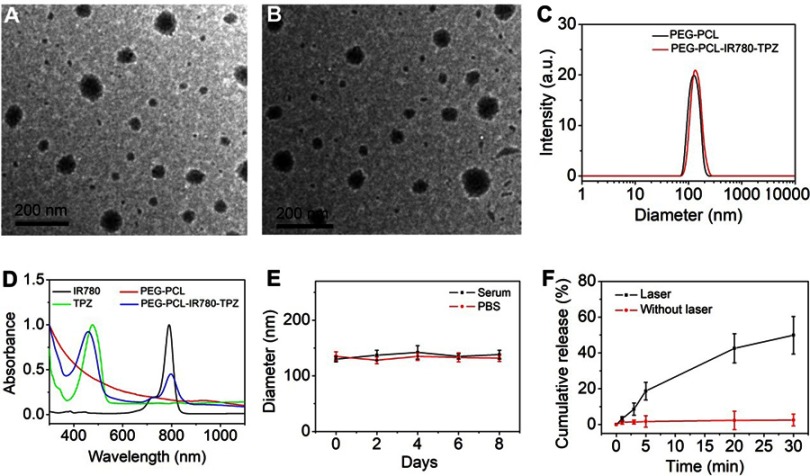
Figure 2.
(A) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) photograph of PEG-PCL NPs. (B) TEM photograph of PEG-PCL-IR780-TPZ NPs. (C) Dynamic light scattering (DLS) of PEG-PCL NPs and PEG-PCL-IR780-TPZ NPs. (D) UV-vis-NIR absorption spectra of PEG-PCL (deionized water as solvent), IR780 (dichloromethane as solvent), TPZ (dichloromethane as solvent), and PEG-PCL-IR780-TPZ NPs (deionized water as solvent). (E) Stability of PEG-PCL-IR780-TPZ NPs in fetal bovine serum (FBS) or phosphate buffer saline (PBS) was monitored by the DLS technology. (F) The release profile of polyethylene glycol- polycaprolactone-2-[2-[2-Chloro-3-[(1,3-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl-1-propyl-2H-indol-2-ylidene)ethylidene]-1-cycloxen-1-yl]-ethenyl]-3,3-dimethy-1-propyl-1H-indolium iodide-tirapazamine nanoparticles (PEG-PCL-IR780-TPZ NPs) under an 808 nm laser irradiation (1 W/cm2).