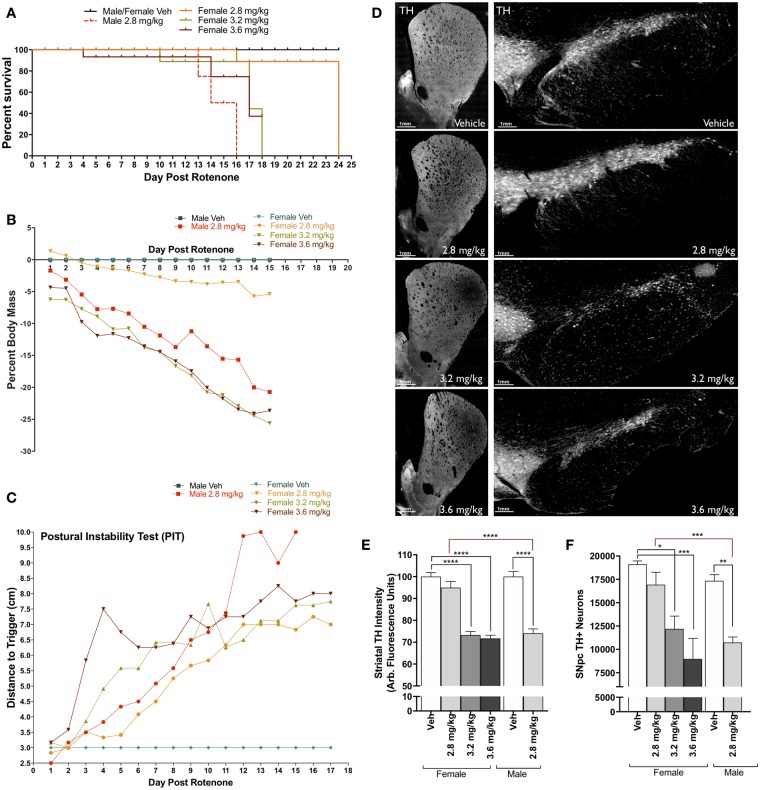
Figure 2.
Establishing rotenone-induced neurodegeneration within female Lewis rats. A, Survival plot of male and female Lewis rats following daily rotenone injection of 2.8 mg/kg (orange), 3.2 mg/kg (green), 3.6 mg/kg (maroon), or vehicle (black), compared to 2.8 mg/kg in male rats (red). B, Percent loss of body mass of male and female rats over 15 days of rotenone treatment. C, Postural instability test (PIT) motor-behavior scoring following rotenone treatment of male and female rats. D, Representative striatal tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive terminal and substantia nigra (SN) montage images (×20) from female rats dosed with vehicle, 2.8 mg/kg, 3.2 mg/kg, and 3.6 mg/kg rotenone. E, Average intensity values of quantified TH in striatal terminals (F(1, 238) = 90.61, p < .0001; two-way analysis of variance [ANOVA]). F, Stereological counts of TH-positive neurons within the SN (F(1, 24) = 6.946, p = .0145; two-way ANOVA). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)