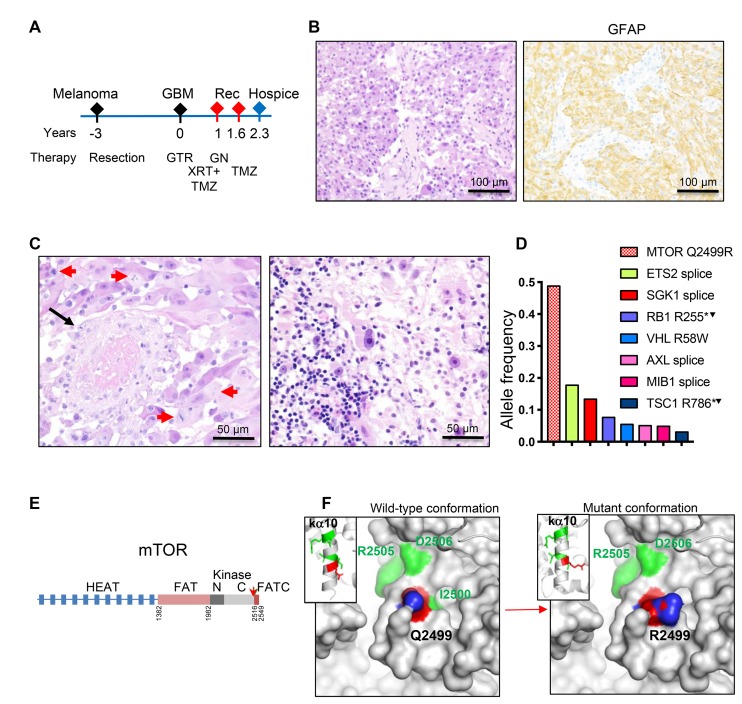
Figure 3. Patient 3: Intraventricular glioblastoma with MTOR mutation and over 2-year survival.
(A) Time course of clinical progression, including the prior resection for thigh melanoma. Abbreviations: Rec, recurrence; GTR, gross total resection; GN, gamma knife; XRT, radiotherapy; TMZ, temozolomide. (B) Resection H&E and IHC show diffuse SEGA-like morphology of neoplastic cells that are positive for GFAP. (C) H&E also shows vessel thrombosis (black arrow), numerous mitotic figures (red arrows) and prominent infiltration with lymphocytes (right panel). (D) NGS reveals a missense MTOR driver mutation, and multiple subclonal mutation. Superscript arrowhead indicates loss of the chromosomal locus for the respective gene (see also Supplementary Table 2). (E) Structural mapping of the novel mTOR Q2499R mutation. Domain map of mTOR: HEAT (Huntigtin, elongation factor 3, protein phosphatase 2A, TOR1) repeats, FAT (FRAP, ATM, TRRAP) domain, N- and C-terminal lobes of the kinase domain and FATC C-terminal domain. Amino acid boundaries are indicated. The Q2499R mutation is shown by red arrow. (F) Ribbon (insets) and surface 3D representations of mTOR last alpha helix of the kinase domain (ka10) oriented to view the positioning of 5 backbone residues mutated in human cancer: Q2499 in red, and I2500, I2501, R2505 and D2506 in green, as well as and their projection to the surface. The surface representation panels show that the Q2499R mutation induces a significant surface conformational and net charge change, with replacement of the hydrophobic wild-type relief formed by Q2499 and I2500 side chains with a positively-charged patch from the R2499 side chain. The side chain labeling: O atoms in red, N atoms in blue.