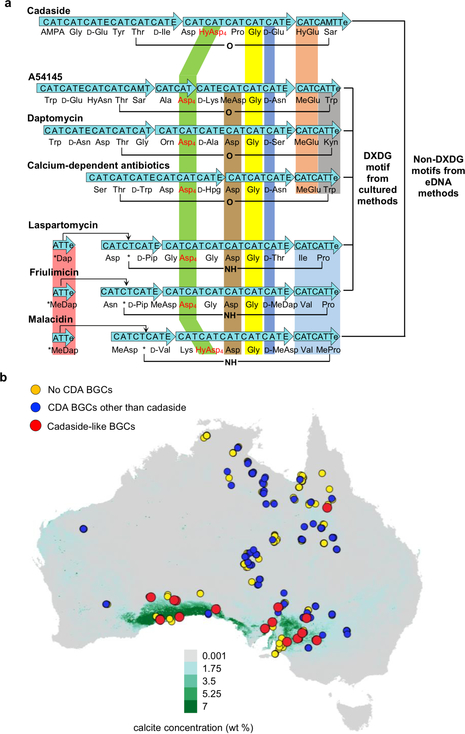
Figure 5.
a) Comparison of calcium-dependent antibiotic biosynthetic gene clusters and the metabolites they encode. b) DNA was extracted from soils collected at 397 sites across Australia and the presence of calcium-dependent antibiotic biosynthetic gene clusters in soils was predicted based on AD domain sequencing. Each collection site is superimposed on a map of Australia that was color coded according to the predicted environmental calcium carbonate concentration (green for high calcium, grey for low calcium).55 At this scale an individual spot can represent multiple different collection sites. If a calcium-dependent antibiotic AD domain sequence was found at any overlapping site, the spot at that site was colored to represent this observation.