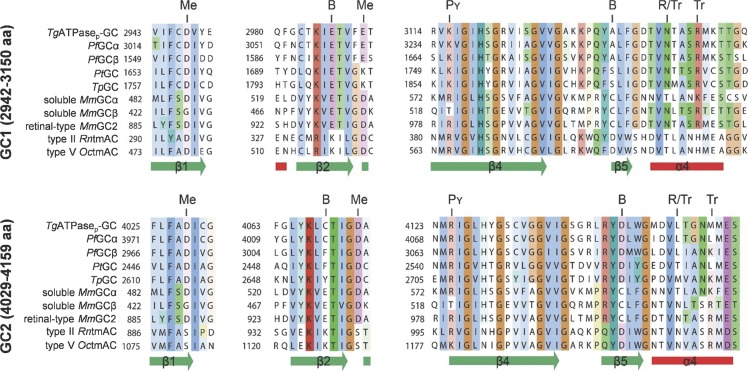
Figure S3. The sequence alignment of GC1 and GC2 domains from TgATPaseP-GC with other representative cyclases identifies signature residues.
Amino acid sequences were aligned with the Clustal Omega program. The color-coding refers to conserved residues. The secondary structures depicted underneath the alignment correspond to the type III tmAC (UniProt-Protein Data Bank ID: 1AZS, Oryctolagus cuniculus for GC1, Rattus norvegicus for GC2; DSSP hydrogen bond estimation algorithm). In type III cyclases, seven residues are involved in cofactor binding for the catalysis, which are indicated above the alignments as “Me” for metal, “B” for base, “Pγ” for phosphate, “R” for ribose, and “Tr” for transition state binding. Note that alignment of GC1 and GC2 domains from TgATPaseP-GC to their orthologous GCs/ACs showed that unlike other cyclases, a 74-residue-long segment (3,033–3,107 aa) is inserted between α3 and β4 of GC1 (not shown). Organism abbreviations and accession numbers: TgATPaseP-GC, T. gondii (UniProt; S7VVK4); PfGCα, P. falciparum (AJ245435.1); PfGCβ, P. falciparum (AJ249165.1); PtGC, Paramecium tetraurelia (XP_001346995.1); TpGC, Tetrahymena pyriformis (AJ238858.1); soluble MmGCα, Mus musculus (AAG17446.1); soluble MmGCβ, M. musculus (AAG17447.1); retinal type MmGC2, M. musculus (NP_001007577.1); type II RntmAC, Rattus norvegicus (P26769.1); and type V OctmAC, Oryctolagus cuniculus (CAA82562.1).