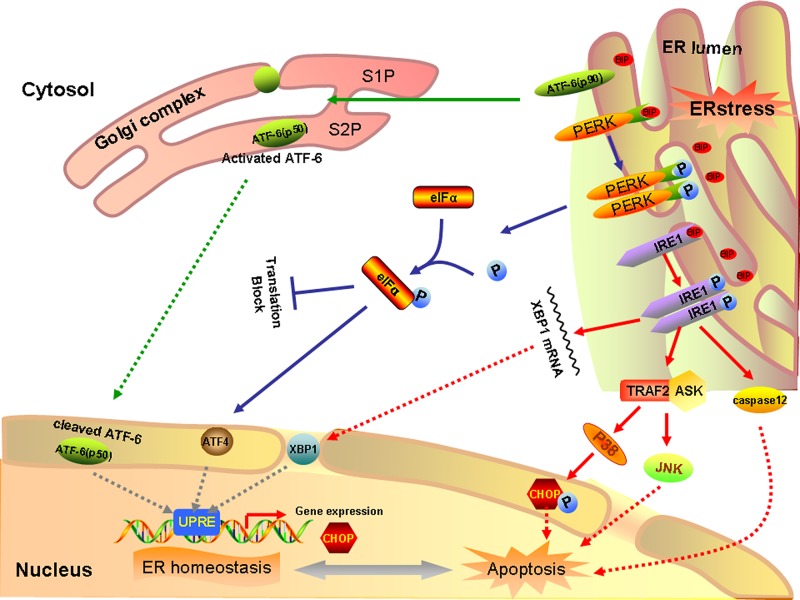
Figure 8. A schematic of unfolded protein response signaling pathway.
In response to ER stress, Bip dissociates from ER stress transducers and binds to unfolded and misfolded proteins, resulting in the activation of ER stress transducers PERK, IRE1 and ATF6. Upon activation, PERK increases phosphorylation of eIF2α, leading to a global attenuation of protein synthesis and a concomitant increase in ATF4 translation. In turn, ATF4 induces CHOP, a proapoptotic transcription factor. After the dissociation of Bip, IRE1 splices the mRNA of XBP1, and produces an active transcription factor named spliced XBP1, which upregulates ER chaperones and proteins implicated in the ER-associated protein degradation. Furthermore, IRE1 recruits TRAF2 to trigger activation of ASK1 and JNK resulting in SGC apoptosis. Meanwhile, TRAF2 liberates procaspase 12 and allows its dimerization and translocation in the cytosol, finally leading to apoptosis. Besides, ASK1 can also activate p38, the activated state of which functions to phosphorylate CHOP, thereby enhancing its pro-apoptotic effect. In addition, ATF6 translocates to Golgi apparatus, where it is activated by site 1 and site 2 Golgi resident proteases. Activated ATF6 transcriptionally induces ERAD genes and upregulates CHOP expression.