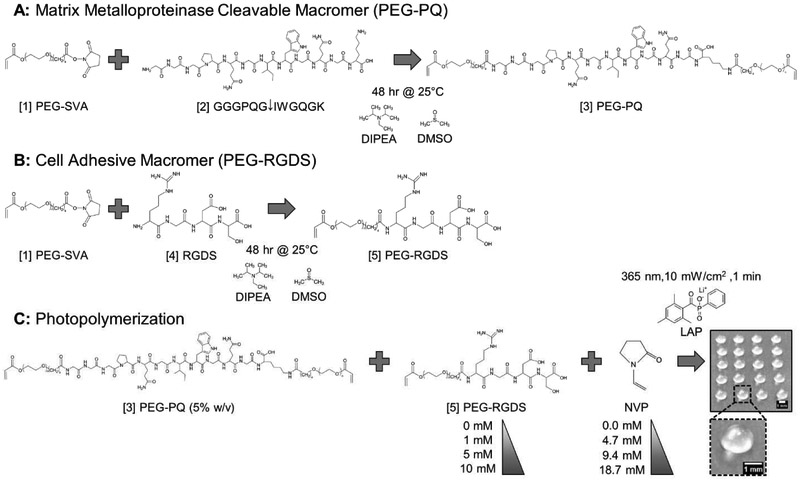
Fig. 1: Macromer Synthesis & Hydrogel Photopolymerization.
(A) [1] Acrylate-PEG-SVA (PEG-SVA) was reacted with the matrix metalloproteinase cleavable peptide sequence, [2] GGGPQGIWGQGK (PQ), to yield the [3] PEG-PQ macromer consisting of the PQ sequence flanked by two PEG chains, each containing a terminal acrylate group. (B) A similar reaction was performed with the integrin ligating peptide sequence, [4] RGDS, to yield the [5] PEG-RGDS macromer with one PEG chain with a terminal acrylate group. (C) [3] PEG-PQ (5% w/v) and [5] PEG-RGDS (0-10 mM) were photocrosslinked with the comonomer n-vinyl pyrrolidinone (NVP) (0.0-18.7 mM) via photoinitiation of lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl phosphinate (LAP) to generate 3 μL hydrogel droplets with a diameter of ~1.5 mm and height of ~1 mm (Scale bar = 1 mm). MDA-MB-231 cells were encapsulated at a density of 10×106 cells/mL and the hydrogels transferred to media containing wells for culture and subsequent analysis.