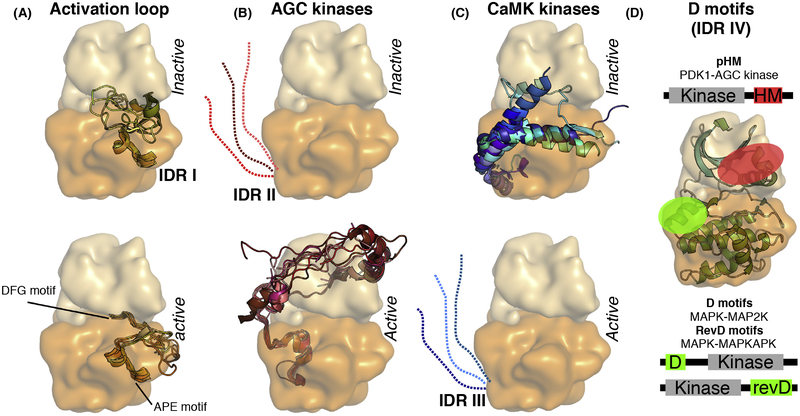
Figure 2. Types of Known Protein Kinase IDRs.
Universal or kinase group specific IDRs often have distinct structural propensity in the inactive versus active state of the kinase. (A) For example, the flexible activation loop of most kinases shows a greater structural propensity in their active versus inactive state (IDR I). (B) Similarly, the C-terminal extension of AGC kinases contains SLiM (pHM), which is more flexible in the inactive state but it can interact with the N lobe in a phosphorylation-dependent manner and becomes ordered in the active conformation (IDR II). (C) In contrast, the C tail of CaMK forms a helical extension in the inactive kinase and this blocks the active site (IDR III). In this case, coactivator binding (e.g.,calmodulin) activates the kinase by competing with the inhibitory helix, thus releasing the steric inhibition (panels were made by using the following protein structures from the PDB: 1ATP, 1IRK, 1QCF, 1OPJ, 1ERK, 1IR3, 2ERK, 2OFV, 3MPM, 3DQW for panel A; 1ATP, 1YM7, 2ACX, 2VD5, 2ESM, 3D0E, 3QKM, 3IW4, 3TXO, 3PFQ, 4L45for panel B; 1TKI, 1KWP, 2VZ6, 2W4K, 2YA9, 2W40, 3RNY, 3KN5, 3MFR, 3BHH, 4MAO for panel C). (D) D motifs are short protein regions located in the IDRs of kinase-binding proteins and they bind to dedicated protein-protein interaction surfaces on kinases. Different kinases may have distinct surface grooves for D motif binding. For example, pHM binds to the PIF pocket located on AGC kinases (shown in red), while unphosphorylated HM binds to the active site cleft of an activator kinase (such as the C-terminal kinase of ribosomal S6 protein kinase). In contrast, the N-terminal D motif from the activator kinases (MAP2Ks) and the C-terminal D motif from the downstream substrate kinases (MAPKAPKs) of MAPKs both bind to another docking surface (shown in green). MAPK-binding D motifs may bind the same so-called docking groove on the kinase in two different N-to-C-terminal orientations (D motifs versus reverse D-motifs, RevD). Abbreviations: AGC kinases, protein kinase A, G and C family; CaMK, calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase; D motif, docking motif; IDR, intrinsically disordered region; MAP2K, MAPK kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MAPKAPK, MAPK activated protein kinase; pHM, phosphorylated hydrophobic motif; PIF pocket, PDK1 interacting fragment pocket; SLiM, small linear motif.