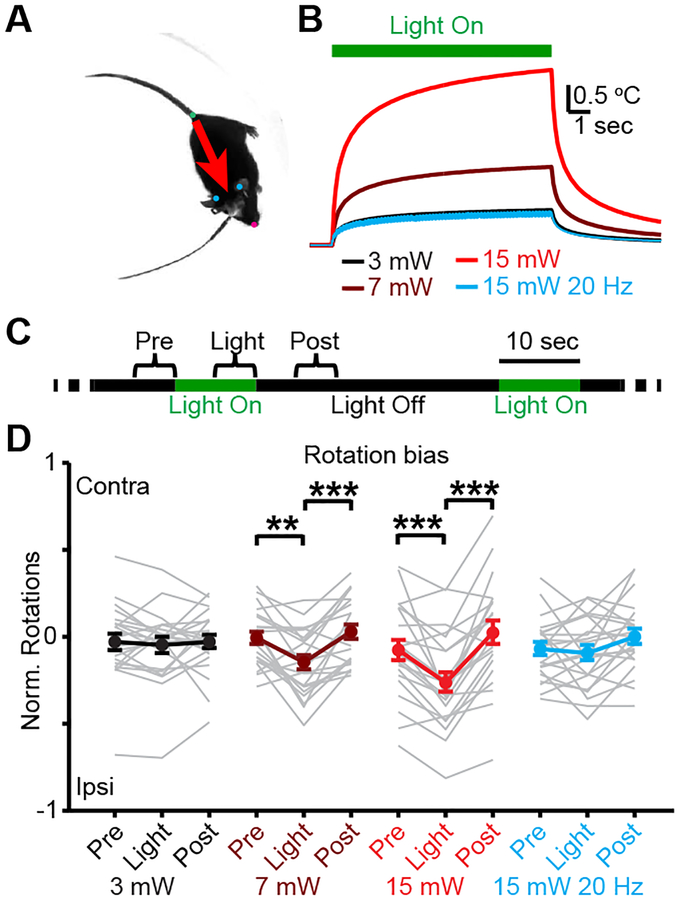
Figure 3: Light delivery in dorsal striatum drives rotational behavior.
A. Video frame illustrating body position tracking. B, Modeled temperature change1 for continuous or pulsed light delivery at 532 nm. Duty cycle was 20% for pulsed light. C, Light delivery protocol for open field behavioral tests. D, Mean rotational bias in response to light delivery. Two-sided signed-rank test (N=11 mice, 2 hemispheres per mouse, n=22 sessions per condition; 3 mW, P=0.37 and P=0.66; 7 mW, P=2.7×10−3 and P=3.9×10−4; 15 mW, P=2.3×10−4 and P=1.1×10−5; 15 mW at 20 Hz, P=0.94 and P=0.06). ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001. Error bars and shaded regions are s.e.m.