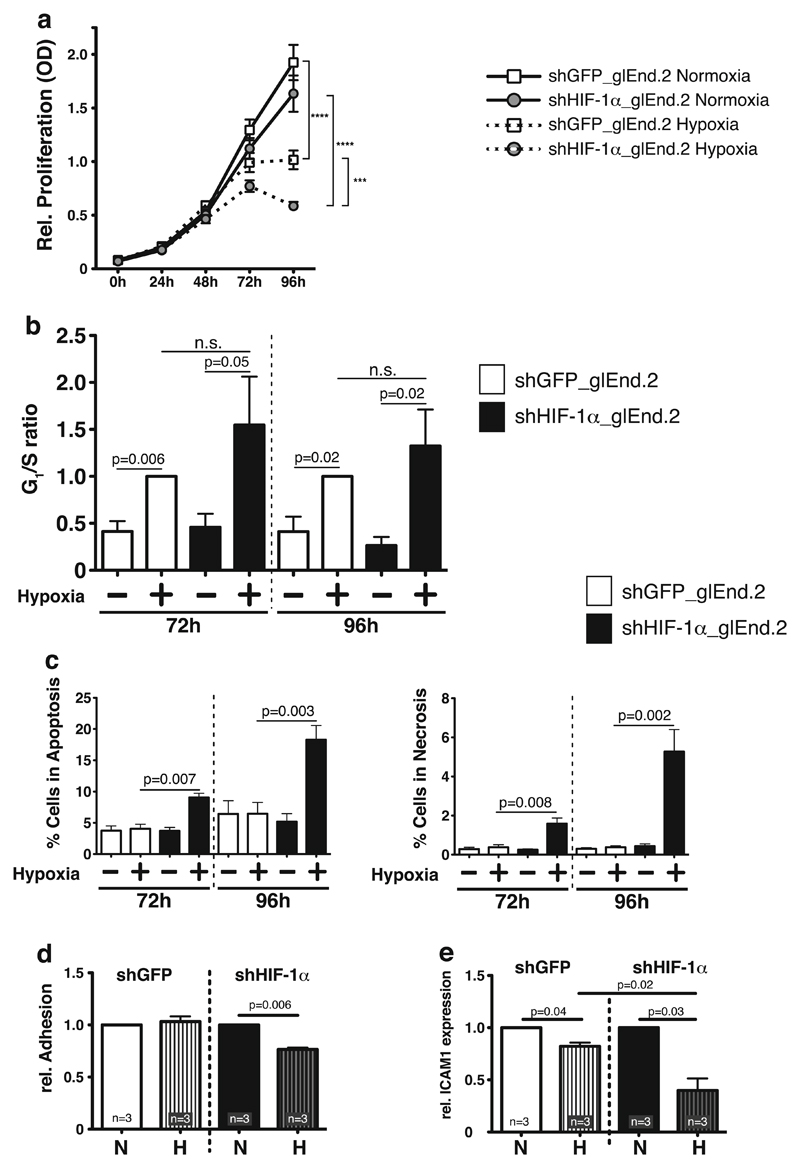
Fig. 1. Effects of HIF-1α deletion in glomerular microvascular endothelial cells (glEND.2).
a Deletion of HIF-1α in glEND.2 does not affect normoxic proliferation. Hypoxia significantly reduces proliferation starting at 72 h and continuing until 96 h. Deletion of HIF-1α further reduces hypoxic proliferation (n=9–11 per group). b In hypoxic wild-type glEND.2 cells (open bars) G1/S ratio, which indicates cell cycle arrest, is significantly induced compared to normoxia after 72 and 96 h. Deletion of HIF-1α (closed bars) does not significantly change the hypoxic G1/S ratio, thus hypoxic cell cycle arrest is independent of HIF-1α (n >3 per group). c Deletion of HIF-1α (closed bars) significantly induces apoptosis and necrosis in glEnd.2 cells during prolonged hypoxia (n=4–5). d Adhesion of primary macrophages to glEND.2 cells is significantly reduced in hypoxia after deletion of HIF-1α (n =3). e mRNA expression of ICAM1 in glEND.2 cells is significantly reduced after 18 h of hypoxia. Deletion of HIF-1α further reduces hypoxic ICAM1 expression, which indicates that HIF-1α stabilization prevents ICMA1 downregulation in hypoxia (n=3)