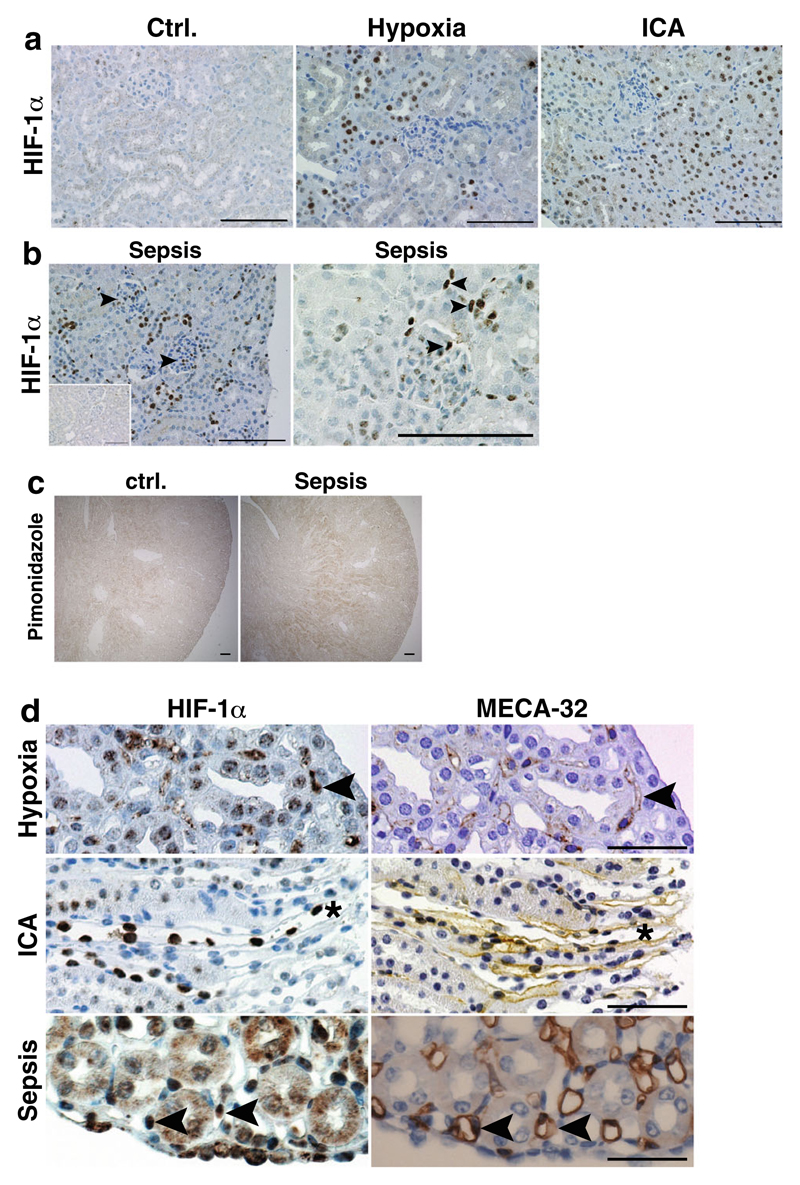
Fig. 2. HIF-1α activation in wild-type kidneys after different stimuli.
a No HIF-1α protein is observed in control conditions. Global HIF-1α activation is more profound after PHD inhibition with ICA than in hypoxia. The majority of HIF-1α protein is detectable in tubular epithelial cells. No glomerular or interstitial HIF-1α staining is visible in hypoxic and ICA-treated kidneys (×400, scale bar 100 μm). b In septic kidneys, tubular, glomerular, and interstitial HIF-1α positivity is observed (arrowheads; ×400, scale bar 100 μm; inset—sham kidney). c Pimonidazole staining confirms hypoxic areas in kidneys of mice treated with CLP-induced sepsis compared to control kidneys (×40, scale bar 100 μm). d Serial sections stained for HIF-1α (left) or the endothelial marker MECA-32 (right) shows specific HIF-1α protein expression (arrowheads) in medullary/papillary EC after stimulation with hypoxia or PHD inhibitors (asterisk denotes the same vessel) or after CLP-induced sepsis (representative images, ×400, scale bar 50 μm)