Figure 8.
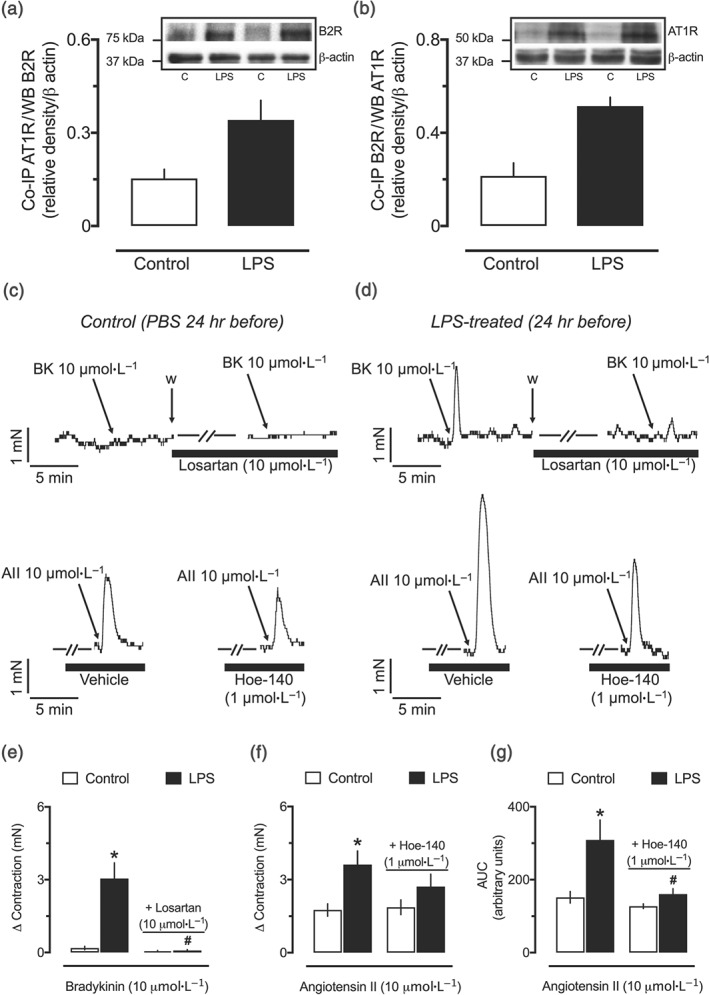
Biochemical and functional evidence of interaction between B2 and AT1 receptors in resistance arteries from endotoxemic female rats. Densitometric analyses and representative Western blots of lysates of resistance mesenteric arteries subjected for co‐immunoprecipitation (Co‐IP) using anti‐AT1 receptor antibodies and detected by an anti‐B2 receptor antibody (a) or Co‐IP using anti‐B2 receptor antibody and detected by an anti‐AT1 receptor antibody (b). Representative tracings showing the effect of 10‐μmol·L−1 bradykinin without or with incubation with 10‐μmol·L−1 losartan, upper traces in (c) and (d), or 10‐μmol·L−1 angiotensin II without or with incubation of 1‐μmol·L−1 Hoe‐140, lower traces in (c) and (d), in endothelium‐intact small mesenteric arteries obtained from the control (c) and LPS‐treated (d) rats. Losartan‐sensitive contractile effects of bradykinin (e) and Hoe‐140‐sensitive enhancement of angiotensin II‐induced vasoconstriction (f, g) in small mesenteric arteries from endotoxemic rats. Small mesenteric arteries were obtained from female rats 24 hr after intraperitoneal administration of LPS (1 mg·kg−1) or PBS (1 ml·kg−1, control group). Co‐IP was performed in samples from eight different animals per group: four used with the anti‐ AT1 receptor antibody (a) and four with the B2 receptor antibody (b). The experiments in organ baths (e–g) were conducted with resistance arteries obtained from six different animals per group. All panels show the mean ± SEM. *P < .05, significantly different from the control group; # P < .05, significantly different from the respective group without incubation with losartan or Hoe‐140; one‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post‐test (e–g)
