Figure 10.
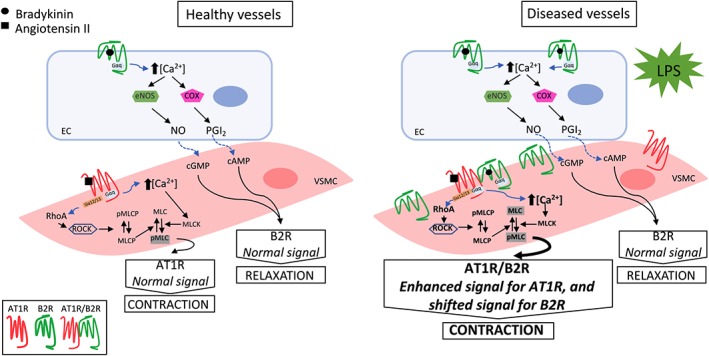
Schematic proposal of the mechanisms involved in the development of secondary pressor responses to bradykinin after endotoxin challenge. Increased levels of B2 receptors and occurrence of the AT1 / B2 receptor complexes (heterodimers) disclose a novel “biochemical fingerprint” in resistance arteries from endotoxemic rats (right), compared with healthy arteries obtained from non‐endotoxemic animals (left). The enlarged arrow indicates the potentiation of angiotensin II‐induced contraction. This hypothetical model of AT1 / B2 receptor heterodimerization is supported by in vivo and in vitro results obtained in this study, using both pharmacological and biochemical approaches. AT1R, angiotensin II AT1 receptor; B2R, bradykinin B2 receptor; EC, endothelial cell; eNOS, endothelial NOS; MLC, myosin light chain; MLCK, myosin light chain kinase; MLCP, myosin light chain phosphatase; PGI2, prostacyclin; pMLC, phosphorylated myosin light chain; pMLCP, phosphorylated myosin light chain phosphatase; RhoA, small G protein; ROCK, Rho‐associated kinase; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell
