Figure 2.
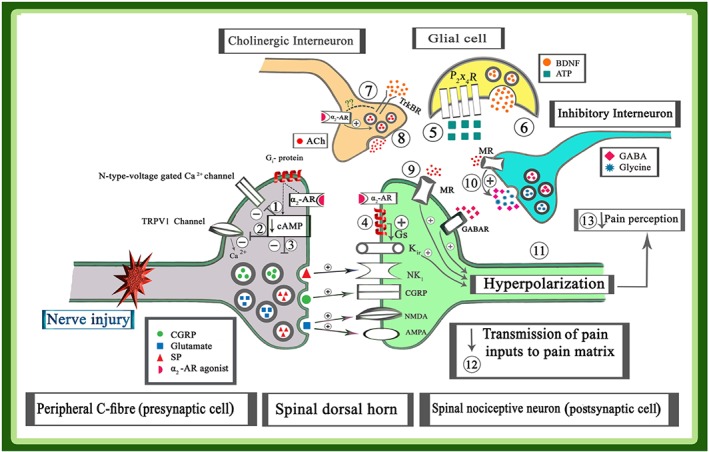
Cellular mechanisms for analgesic effects of α2‐adrenoceptor (AR) agonists; α2‐adrenoceptors located both in the peripheral sensory neurons and spinal neurons. The activation of α2‐adrenoceptors on presynaptic cells, using an α2‐adrenoceptor agonist, reduces the activity of AC, suppressing both the production of the cAMP and the activity of PKA. Then, suppressing the activity of PKA inhibited the presynaptic N‐type voltage‐gated Ca2+ channels (1) and TRPV1 channel activity (2); subsequently, the influx of Ca2+ ions to presynaptic cell and the release of stimulators neurotransmitters such as glutamate, substance P, and CGRP from primary fibre terminals in the spinal cord are decreased (3). Furthermore, application of α2‐adrenoceptor agonist increases the activity of Gs proteins in the postsynaptic cells. Activation of Gs protein, increased both the production of the cAMP and the activity of PKA, and then the activity of K+ ir channels and efflux of K+ ions are increased. Efflux of K+ ions induced hyperpolarization in the postsynaptic neurons (4). Nerve injury increased the release of ATP from the peripheral sensory neuron and also induced an up‐regulation of P2X4 receptors on glial cells (5). The activity of P2X4 receptors increased the release of BDNF from glial cells (6). At the same time, activation TrkB receptors on cholinergic interneurons (7) and its interaction with α2‐adrenoceptors via unknown mechanisms elicited the release of ACh (8). Activation of muscarinic receptors directly on the postsynaptic cells (9) or indirectly on the inhibitory GABAergic or glycinergic interneurons (10) can also induce hyperpolarization in the postsynaptic cells (11). Therefore, the application of an α2‐adrenoceptor agonist elicited hyperpolarization in the postsynaptic cell via above‐mentioned mechanisms. Hyperpolarization of the neuron decreased transmission of pain inputs to higher centres (12) and suppressed pain perception (13)
