Figure 2.
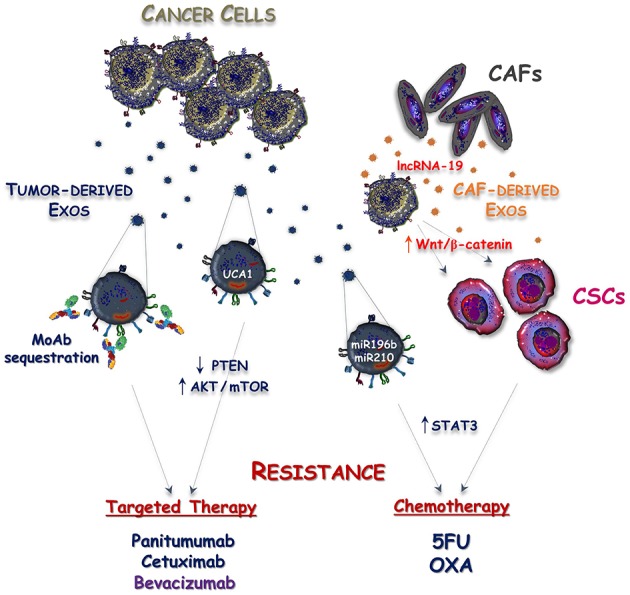
Mechanisms responsible for Exosome-mediated drug resistance in CRC. Exosomes released by either tumor cells (Tumor-derived Exos) or cancer associated fibroblasts (CAF-derived Exos) cooperate to induce resistance of CRC against targeted and cytotoxic drugs. This process is mediated by exosomal delivery of non-coding RNAs into cancer cells leading to the stimulation of mTOR and STAT3 intracellular signaling, as well as to the acquisition of cancer stemness features. Additionally, sequestration of anti-EGFR (panitumumab and cetuximab) and anti-VEGF (bevacizumab) monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) by Tumor-derived Exos is another possible mechanism reducing the bioavailability of these drugs and defective anti-cancer activity.
