FIG 1.
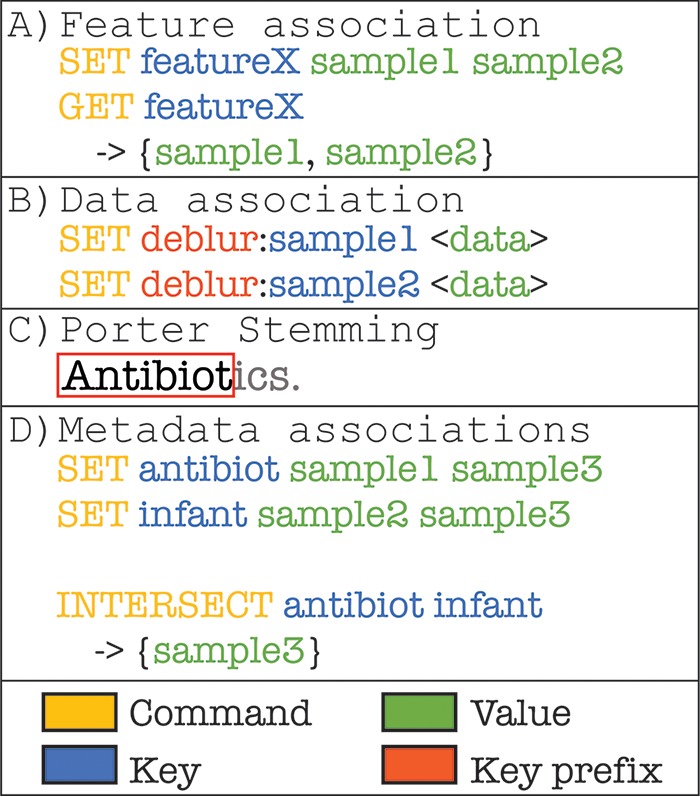
The redbiom data model is a key-value store built on top of Redis. By storing features and sample identifiers as keys, it is possible to rapidly query the resource for information on those entities. Similarly, by indexing the sample metadata, queries can be performed against variables of interest (e.g., pH) in order to identify sample identifiers of interest, which can then be used to extract a feature table for downstream analysis. (A) A “set” command associates a key with a value: in this case, a feature identifier is associated with the samples the feature was observed in. A “get” command can then be issued using the feature identifier as the key to obtain the associated values (i.e., the samples). (B) Feature counts (e.g., a vector from an OTU table) are associated with a composite key that describes the processing context and the sample identifier. The processing context, in this case “deblur,” denotes a bioinformatic procedure applied. For Qiita, the context names also include molecular preparation details. The expectation is the data within a context should be comparable. The sample data themselves are encoded in a sparse vector format with the feature identifiers remapped into unique integers to improve compression and reduce data redundancy. (C) The Porter stem of the word “Antibiotics.” (D) The association of metadata word stems with sample identifiers. Redis natively supports classic set operations, which can be applied to keys to obtain, for example, the intersection of sample identifiers represented by two keys.
