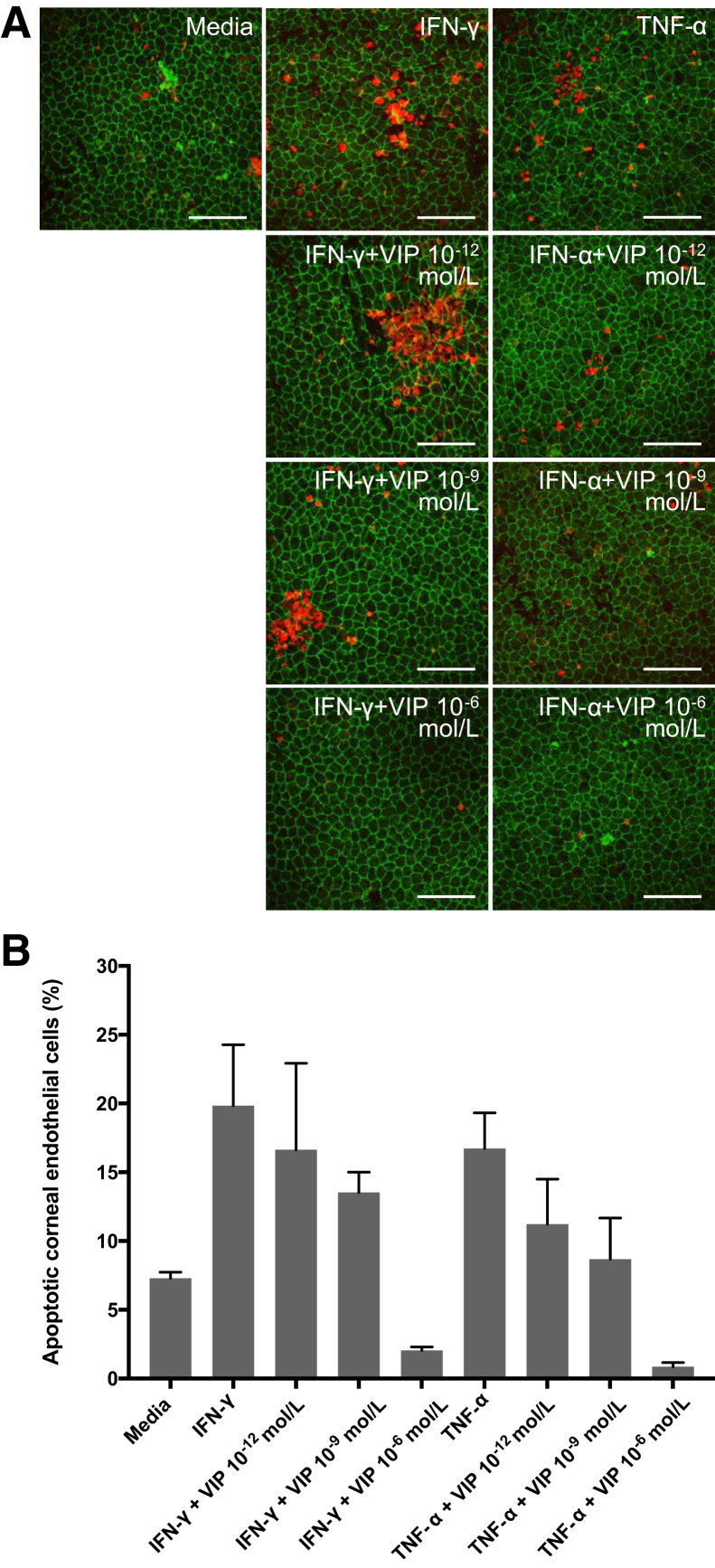
Figure 2.
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) suppresses interferon (IFN)-γ– and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α–mediated corneal endothelial cell apoptosis. A: Representative confocal micrographs showing naïve C57BL/6 corneal cups incubated with IFN-γ or TNF-α with or without VIP (10−12, 10−9, 10−6 mol/L). After 18 hours of incubation, corneas were stained for zonula occluden-1 (green) and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase–mediated dUTP nick-end labeling assay (TUNEL, red) to visualize endothelial cell-to-cell junctions and apoptotic cells, respectively. B: Bar diagram showing the percentages of apoptotic (TUNEL-positive) corneal endothelial cells incubated ex vivo with IFN-γ or TNF-α with different doses of VIP. VIP 10−6 mol/L significantly suppresses IFN-γ– and TNF-α–mediated corneal endothelial cell apoptosis [P = 0.02 and 0.008, respectively (U-test)]. Data are expressed as means ± SEM and data from one of two independent experiments are shown (B). n = 5 corneas (B). Scale bars = 100 μm. Original magnification, ×400.