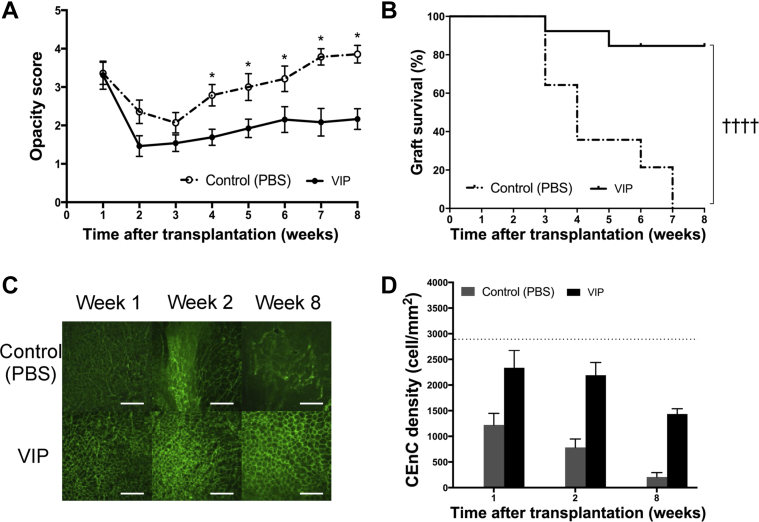
Figure 4.
Effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) treatment on high-risk corneal transplant survival. Animals underwent high-risk allogeneic corneal transplantation and received treatment with VIP at 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 days after transplantation. A: VIP treatment significantly decreases graft opacity scores at 4 to 8 weeks after transplantation. B: Weekly examination of grafts for 8 weeks demonstrates a significant increase in graft survival in VIP-treated mice compared with the controls (85% versus 0%; hazard ratio, 0.10; 95% CI, 0.04–0.26). C: Representative confocal micrographs of central area of transplanted corneas in VIP-treated mice and in controls at 1, 2, and 8 weeks after transplantation. Corneal endothelial cell-to-cell junction were stained and visualized with zonula occluden-1 (green). D: Bar diagram of central corneal endothelial cell (CEnC) densities show significantly higher CEnC density in the VIP-treated group compared with the controls at 8 weeks after transplantation [P = 0.02 (U-test)]. CEnC density in VIP-treated group did not reach statistical significance at weeks 1 and 2 after transplantation compared with the controls (P = 0.11 and P = 0.06, respectively). Horizontal dotted line represents the CEnC density of naïve age-matched C57BL/6 corneas. Data are expressed as means ± SEM and data from one out of two independent experiments are shown. n = 14 (B); n = 5 corneas (D). ∗P < 0.05 versus VIP (U-test); ††††P < 0.0001 (log-rank test). Scale bars = 100 μm (C). Original magnification, ×400 (C). PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.