FIGURE 1.
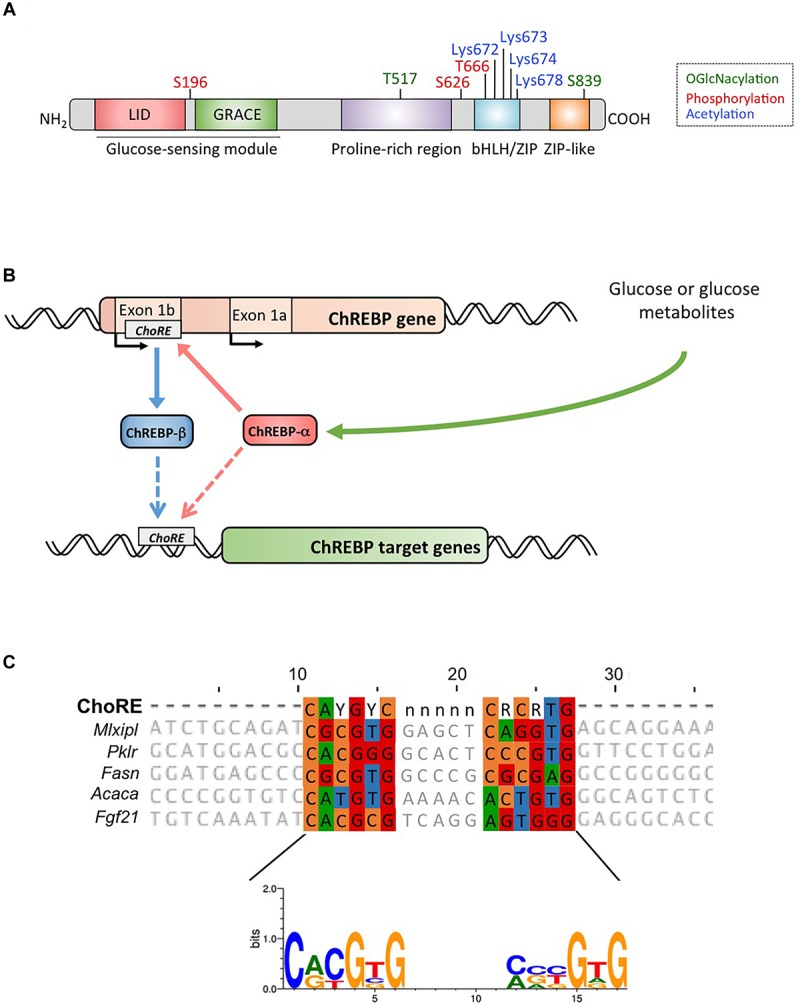
(A) Structure of carbohydrate response element binding protein α (ChREBPα). ChREBPα is composed of 864 amino acids and contains several regulatory domains. At the N-terminus the protein contains a glucose-sensing module composed of the low glucose inhibitory domain (LID) and the glucose activated conserved element (GRACE). The protein also contains a polyproline-rich, a bHLH/LZ and a leucine-zipper-like (Zip-like) domain located at the C-terminus. Post-translational modifications are indicated in their respective residues, phosphorylation (red), acetylation (blue) and the recently identified O-GlcNAcylations (green). (B) Gene structure of the ChREBP gene and generation of the two ChREBP isoforms α and β. ChREBPβ is transcribed from an alternative first exon promoter 1b. This transcript is translated from exon 4 generating a shorter protein of 687 amino acids in which the two NES, the NLS and the LID domain are missing. The ChREBPβ isoform has been suggested to be directly regulated by ChREBPα since a ChoRE sequence was identified in the exon promoter 1b. Whether both ChREBP α and β isoforms both bind to the ChoRE is currently not known. Figure adapted from Herman et al. (2012). (C) Multi-alignment of ChoRE consensus sequences presents in several ChREBP target gene promoters. Nucleotides-based alignment is presented on the top of the figure together with the consensus sequence ChoRE described in Poungvarin et al. (2015). The logo corresponding to the consensus sequence associated to this particular alignment is also represented.
