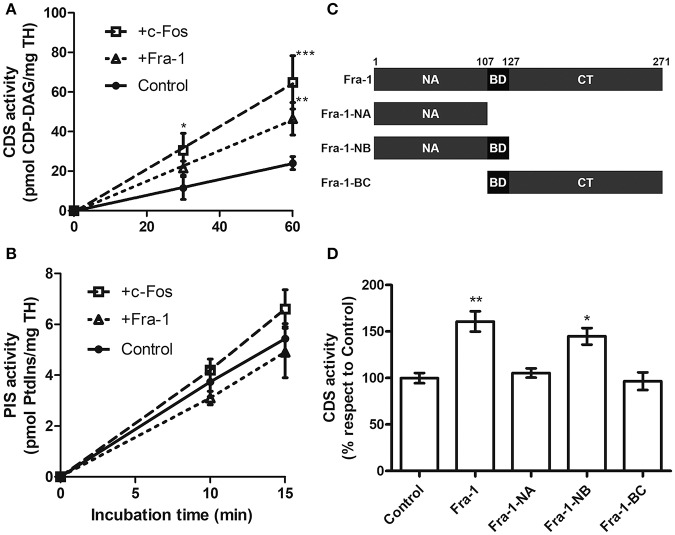
Figure 1.
Fra-1 activates CDS through its NB domain. (A,B) Total homogenate (TH) from quiescent MDA-MB231 cells was used as enzyme source to evaluate total CDS and PIS activity in the presence of Fra-1 (0.5 ng of recombinant Fra-1 per ug of TH; short dashed line) or c-Fos (0.5 ng of recombinant c-Fos per ug of TH; long dashed line) in comparison with the controls that contained only the vehicle used to re-suspend Fra-1 or c-Fos (continuous line). Both c-Fos and Fra-1 significantly activate CDS (A) at the incubation times examined whereas neither of them significantly modified PIS activity (B). (C) Schematic representation of the deletion mutants of Fra-1. The numbers on the top of the scheme indicate the amino acid position. Fra-1-NA: N-terminus (aa 1–107), Fra-1-NB: N-terminus plus basic domain (aa 1–127), Fra-1-BC: basic domain plus the C-terminus (aa 108–271). (D) CDS activity was evaluated in the presence of recombinant Fra-1 or of its deletion mutants. Only Fra-1-NB activates the enzyme to similar levels as those obtained with the full-length version, whereas Fra-1-NA that lacks the BD or Fra-1-BC that lacks the NA do not retain this activating capacity. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (Two-way ANOVA in A,B and 1 way ANOVA in D). Results are the mean CDS activity ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate.