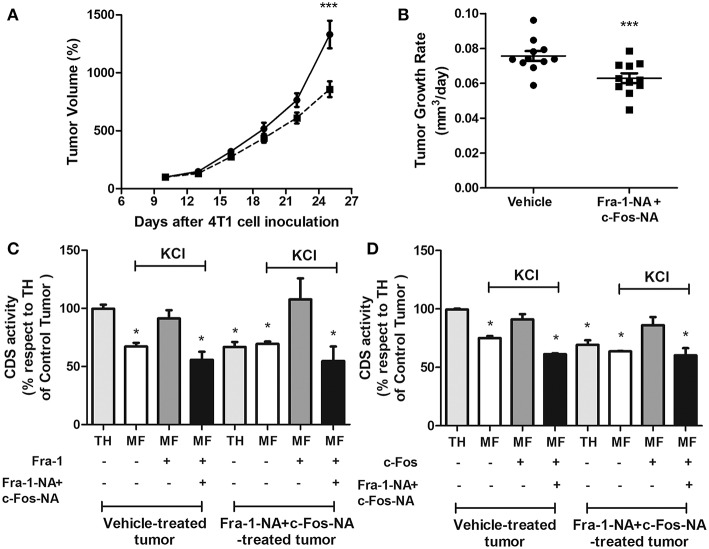
Figure 7.
When grown in the same animal, Fra-1-NA+c-Fos-NA treatment impairs tumor growth and CDS activity. Mice bearing two tumors received intratumoral injections of liposomes containing equal concentrations of Fra1-NA plus c-Fos-NA into one tumor and empty liposomes into the other. Peptide administered: 5 injections containing a total of 9 nmol of Fra-1-NA plus c-Fos-NA peptides per injection (dashed line) or vehicle (continuous line) delivered three times a week for 15 days. (A) Tumor volumes were measured at 3-day intervals during the treatment period. Results are expressed as the percent volume taking the volume of the tumor at 10 days of inoculation as 100%. ***p < 0.001 (Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post-test) (B) Tumor growth rates were calculated for each group at the end of the treatment as the slope of the curve obtained by plotting the log10 of the tumor volume in function of the days of treatment. Horizontal bars represent mean values. ***p < 0.001 (Paired t-test). Mice examined: n = 11. (C,D) CDS activity was measured in TH (light gray bars) and the microsomal fraction (MF) stripped with KCl 1M (white, dark gray and black bars) from vehicle-treated tumors and Fra-1-NA plus c-Fos-NA-treated tumors of two mice. Recombinant wild type Fra-1 (C), recombinant wild type c-Fos (D) and/or Fra-1-NA + c-Fos-NA (C,D) were added to the reaction as indicated in the figure. Experiments were performed in triplicate; bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM. All experimental situations were compared to TH from the non-treated samples. *p < 0.05 (One-way ANOVA, Dunnett post-test).