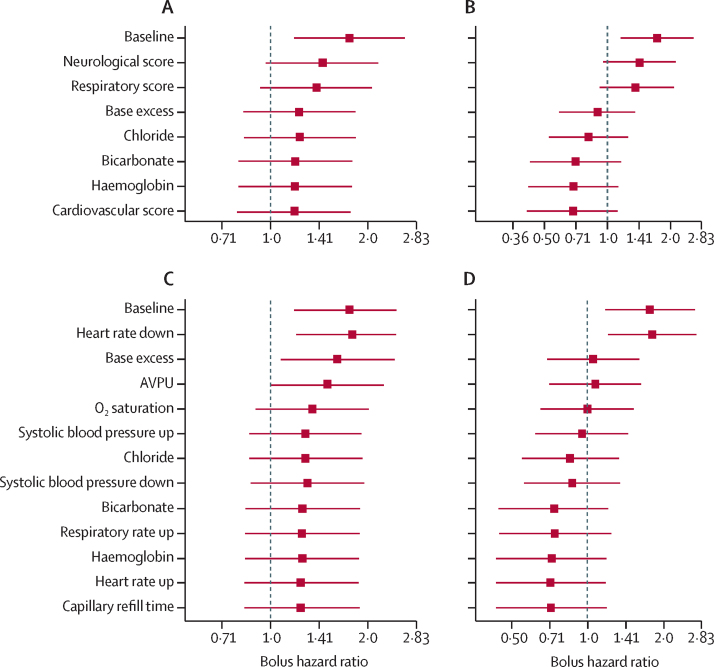
Figure 4.
Contribution of physiological derangements to excess mortality due to bolus
In post-hoc analyses, we calculated hazard ratios for bolus versus no bolus on time of death in Cox proportional hazard models, sequentially incorporating additional explanatory covariates (in order from top to bottom of each list), showing how the effect of bolus on death is mediated by observed changes in physiology and blood parameters (A–D). Up or down refers to the direction of change from the age-related mean values, which contribute to different physiological scores. (A) The covariate list includes physiological scores at 1 h and conservative (data-derived) estimates of the effect of bolus on blood parameters at 1 h. (B) The covariate list uses literature-derived values for the changes in acid-base biochemistry parameters. (C) The covariate list includes the component variables of the physiological scores at 1 h and conservative (data-derived) estimates of the effect of bolus on blood parameters at 1 h. (D) The covariate list uses literature-derived values for the changes in acid-base biochemistry parameters. Analyses in A–D are based on 1898 subjects with complete data for physiological scores at 1 h and baseline biochemical parameters. AVPU= Alert, Responds to Voice, Responds to Pain, Unresponsive.