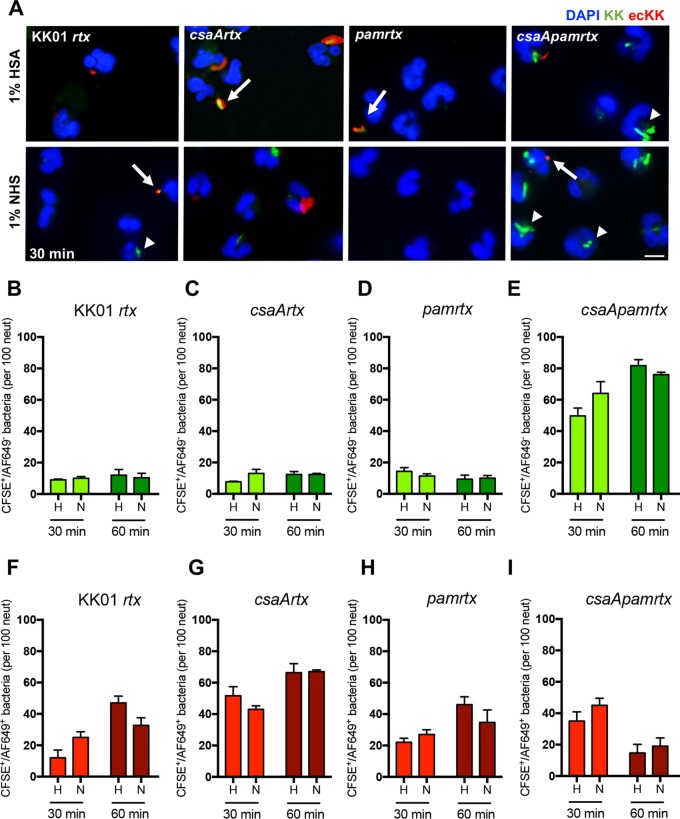
FIG 5.
The presence of the K. kingae surface polysaccharides results in reduced neutrophil association and phagocytosis of K. kingae. Immunofluorescence images (A) are shown along with quantitative analyses (B to I) of K. kingae rtx mutant strains incubated with human neutrophils at an MOI of 10 for 30 min or 60 min, as indicated, in the presence of 1% HSA or 1% NHS. K. kingae strains were stained with CFSE (green) prior to infection. Neutrophils were fixed and incubated with a guinea pig anti-K. kingae antiserum and subsequently with anti-guinea pig Alexa Fluor-649 (AF649) to detect extracellular bacteria (red); 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used to stain the nuclei of the neutrophils (blue). Images were acquired using a 20× objective. The arrows indicate extracellular bacteria, and the arrowheads indicate intracellular bacteria. Scale bar, 5 μm. The graphs depict the total number of intracellular (B to E) bacteria and the total number of extracellular (F to I) bacteria for the indicated strains. The data represent the total number of CFSE+ events per 100 neutrophils chosen randomly per biological replicate, and a total of three biological replicates were performed (n = 3). Abbreviations: H, HSA; N, NHS; KK, K. kingae; ecKK, extracellular K. kingae.